(ii) Ground radiation
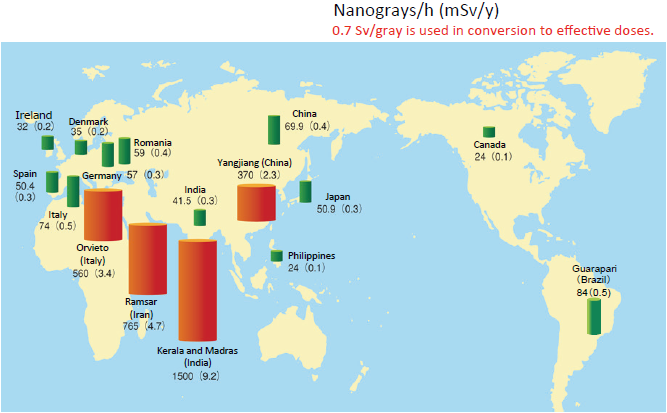
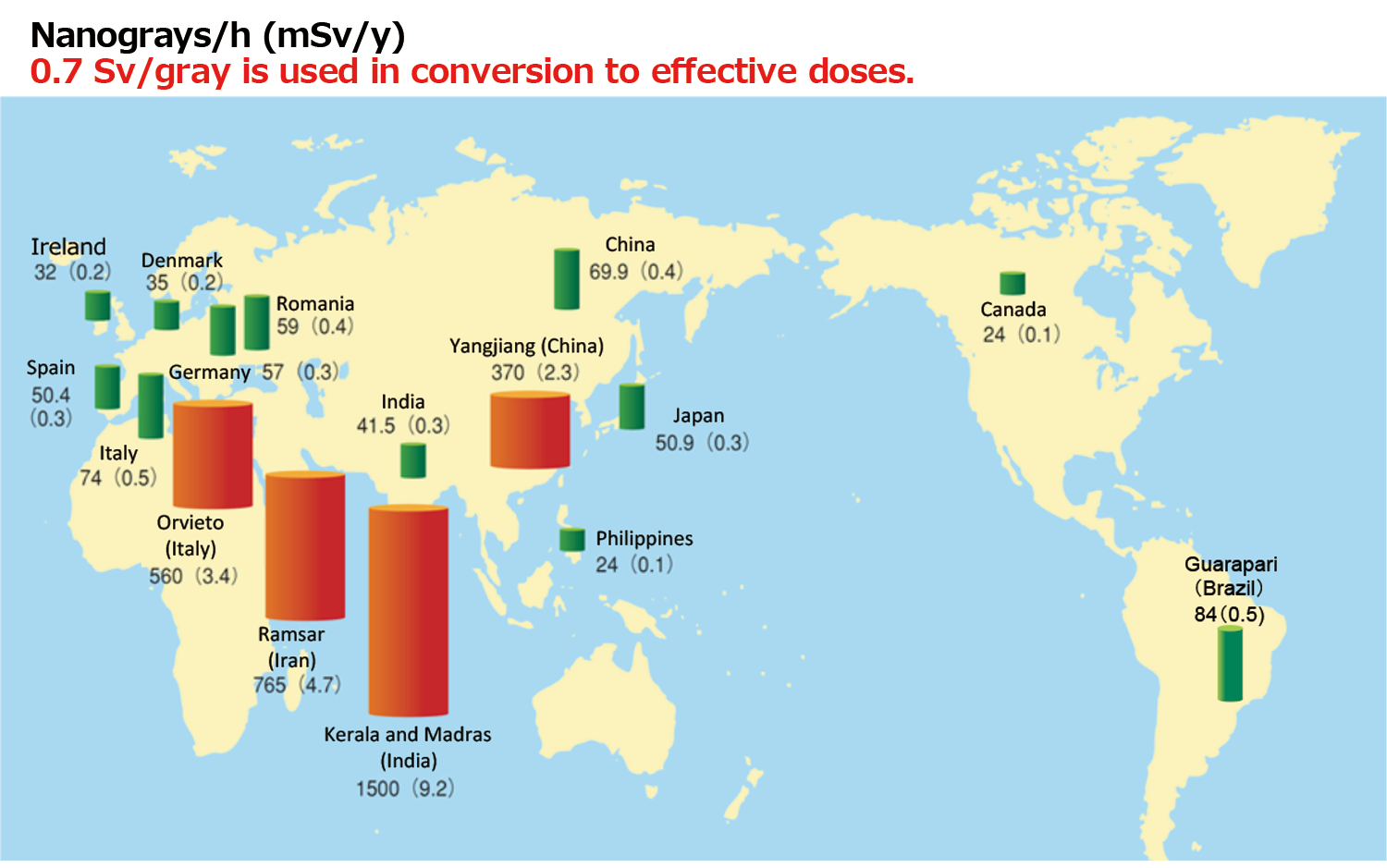
The radiation dose is known to vary between areas as a result of variations in soil and rock composition.
Upon closer inspection, there are major differences in these radiation levels worldwide, and regional differences within Japan as well. In addition, no health effects caused by these differences have been reported.
Ground radiation
- Sources:
- Prepared based on the 2008 UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) Report
and “Environmental Radiation in Daily Life (Calculation of National Doses), ver. 3” (2020), Nuclear Safety Research Association
There are regions around the world where natural radiation is seven to 30 times higher than in Japan, such as Yangjiang in China, Kerala in India, and Ramsar in Iran. The high levels of natural radiation in these regions are due to the fact that soil there is rich in radioactive materials such as radium, thorium and uranium.
For more information about ground radiation around the world, see page 67 of Vol. 1, FY2022 edition.
- Sources:
- From the website of the geological Society of Japan
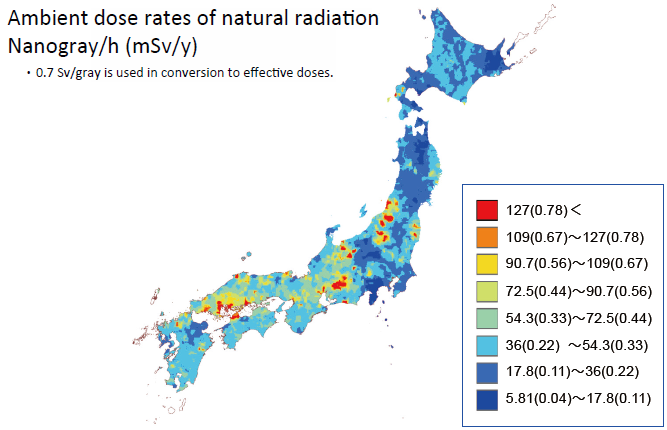
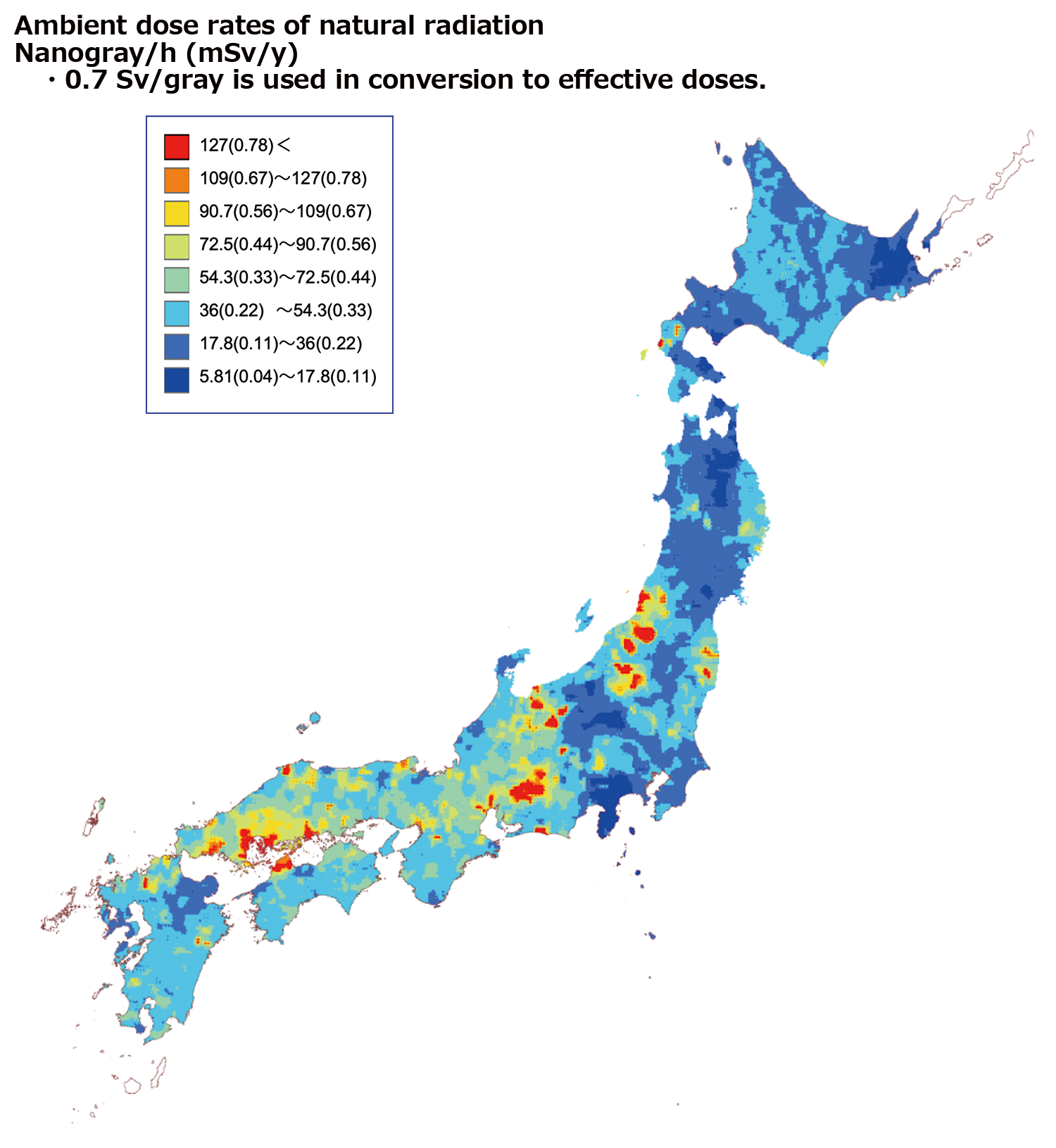
In Japan, like everywhere else, the amount of ground radiation varies from area to area. Comparison of ambient dose rates among different prefectures shows that there is a difference of 0.4 mSv per year between Gifu, where the ambient dose rates are highest, and Kanagawa, where the values are lowest.
For more information about ground radiation in Japan, see page 68 of Vol. 1, FY2022 edition.


