Earth observations using the Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) series
What is the Greenhouse gases Observing Satellite (GOSAT) series?
The mission objective of the GOSAT series of satellites is to contribute to the development of climate change science and policy. It consists of GOSAT (launched in 2009) ,GOSAT-2 (launched in 2018) and GOSAT-GW (launched in 2025), which are currently in operation.
Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite : GOSAT

The greenhouse gases observing satellite mission is jointly conducted by the Ministry of the Environment, NIES, and JAXA in accordance with the Basic Plan for Space Policy to help solve global issues and realize a safe, secure, and prosperous society.
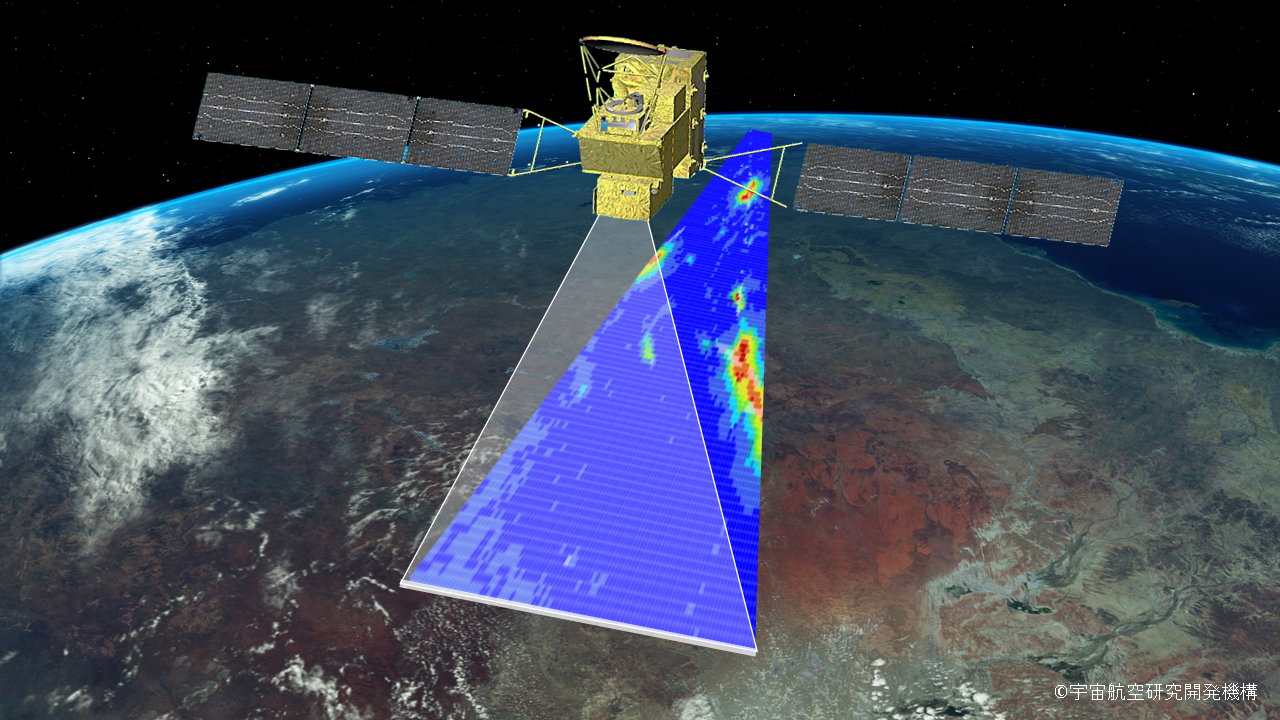
GOSAT
・Analysis of GOSAT observational data provides insights to the global distribution of carbon dioxide and methane, their absorption and emission amounts, and their seasonal and interannual variations.
・This information is used to contribute to climate change science as well as to climate change policy.
・The "2019 Improvements to the IPCC Guidelines for Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Absorption (2006)" which was approved at the 49th IPCC General Assembly meeting held in Kyoto, Japan in 2022, introduced many examples of GOSAT data applications and provided expectations for the GOSAT-2 mission.
・In the "IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) Working Group 1 (WG1) - Natural Scientific Basis", published in August 2021, monthly-averaged GOSAT data on atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane were included among other global datasets demonstrating increases in greenhouse gas concentrations and changes in the rate of increase in the global atmosphere.
・In March 2020 the Ministry of Environment established a study team to discuss how to prevent the GOSAT series from becoming space debris and remaining in orbit indefinitely once the operational period concludes. The team was tasked with examining the issue and making recommendations. In particular, more than 10 years after its launch, a decommissioning plan for GOSAT-1 was identified as a priority. An interim report was compiled in October 2020 and discussions are ongoing with the relevant parties.
(The Ministry of the Environment's Approach to the Space Debris Problem Japanese version English version)
GOSAT-2
・Compared to GOSAT, GOSAT-2 improves the accuracy of carbon dioxide and methane concentration observations with higher-performance onboard sensors. In addition, GOSAT-2 has increased functionality with the ability to concentrate on large emission sources such as major cities and to automatically locate and observe cloud-free areas.
・In order to further improve the ability to identify carbon dioxide emitted by human activities, simultaneous observations of carbon monoxide are also collected.
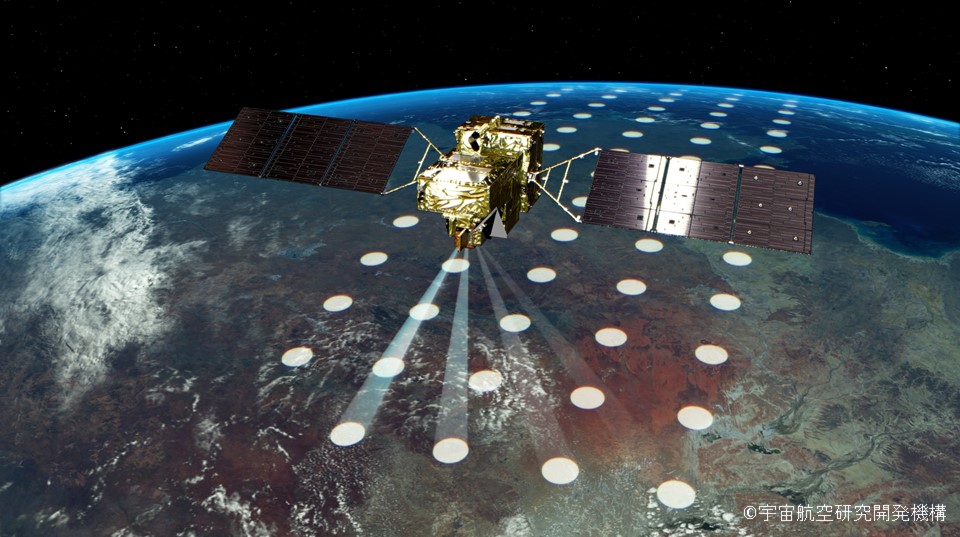

GOSAT-GW
・GOSAT-GW aims to carry on the GHG observations as the successor to the missions of GOSAT and GOSAT-2,
(1)Continuous monitoring of carbon dioxide and methane concentrations in the global atmosphere
(2)Ensuring the transparency of countries' greenhouse gas inventory reporting under the Paris Agreement
(3)Refine climate change projections by monitoring large-scale emission sources.
・Compared to GOSAT and GOSAT-2, GOSAT-GW will allow more precise estimation of carbon dioxide and methane emissions by significantly increasing the number of data. This is intended to make it possible to estimate emissions for countries and regions with small areas, which have been difficult to analyze adequately due to insufficient data, as well as to estimate emissions on a site-by-site basis.
Results of global greenhouse gas observation by GOSAT
Significance and characteristics of GOSAT observations
・Several meteorological organizations around the world, including the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), have calculated and published global average concentrations using ground-based observational data at the earth's surface. However, because the concentration of carbon dioxide varies with altitude, concentration data from ground stations alone does not represent the overall concentration of the Earth's atmosphere.
・In contrast, GOSAT does not measure the surface concentration of carbon dioxide, but rather the total amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from the surface to the top of the atmosphere. The future concentration of carbon dioxide projected in the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the average concentration in the "total atmosphere".
・In order to calculate and predict the risk of global warming due to future increases in greenhouse gases, it is important to calculate the average concentration of greenhouse gases over the entire planet, and it is essential to obtain an average that is representative of the "total atmosphere".
Observation Results ※Links to external webpages
Related Materials and Pages
Introduction Materials and Special Report
- GOSAT Series Introduction Materials (Updated:July 8, 2025) Japanese version English version
- GOSAT-GW Press Open Briefing Material(May 20, 2025)[Japanese Only]
- GOSAT Series Special Report (December 9, 2023 MOE, NIES) Japanese version English version
Poster(s)
- Observing carbon dioxide with GOSAT Series (March 30, 2023) Japanese version English version
Pamphlet(s)
- Up to now and from now on~Observing the global atmosphere with the GOSAT Series~ (March 30, 2023) Japanese version English version
Video(s)
- GOSAT: Advancing the science and policymaking on climate change (Updated:April 28, 2023) Japanese version English version
- Climate Change from Space and Earth: Challenges of the IBUKI series (August 31, 2018)[Japanese Only]
- Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite "IBUKI"-The "eyes" of space watching over the Earth (March 31, 2017)[Japanese Only]
GOSAT Project Press Release
Press release by the Ministry of the Environment(after 2020)
Click here for a list of press releases including project co-implementing organizations- Joint Observations with NASA for GOSAT-GW Data Verification - Observing Greenhouse Gas Sources in Metropolitan Tokyo from the Sky -
- (March 2, 2026).
- Initial Analysis Results of Focus-mode Observeation Data from the Total Anthropogenic and Natural Emissions Mapping SpectrOmeter-3(TANSO-3) Onboard the Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse Gases and Water Cycle(GOSAT-GW, "IBUKI GW")
- (January 8, 2026).
- First observations by the Total Anthropogenic and Natural emissions mapping SpectrOmeter-3 (TANSO-3) onboard the Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle “IBUKI GW” (GOSAT-GW)
- (August 8, 2025). [Japanese Only]
- Launch Result of Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle (GOSAT-GW)
- (June 29, 2025).
- Agreement Reached with UNEP-IMEO and Other Organizations to Utilize GOSAT-GW at the LNG Producer-Consumer Conference 2025
- (June 23, 2025).
- GOSAT 3D Visualizer, which shows the concentration of greenhouse gases, will be exhibited at the Hamagin Space Science center.
- (June 12, 2025). [Japanese Only]
- Launch of the Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle (GOSAT-GW)
- (April 25, 2025). [Japanese Only]
- Annual increase of whole-atmosphere mean concentration of carbon dioxide in 2024 was the largest in the past 14 years: preliminary results from the “IBUKI” (GOSAT) satellite
- (February 6, 2025).
- Signing of the Implementing Arrangement to Continue Collaboration on Satellite Data Comparison of Trace Gases among Ministry of the Environment, JAXA, National Institute for Environmental Studies, and NASA
- (December 12, 2024). Confirmation of Agreement between CO2 Emissions Estimation by GOSAT Series Observation and the Values Report by the Mongolian Government(November 17, 2023).
- The annual increase in the mean concentration of methane in the atmosphere in 2021 has been the largest since 2011 - data from "IBUKI" (GOSAT)(March 10, 2022). [Japanese Only]
- Future Actions on Space Debris Issues by the Ministry of the Environment (Interim Summary)
- (October 15, 2020) [Japanese Only]
Website Links for the project’s partner organizations
National Institute for Environmental Studies,Japan (NIES)
GOSAT Project http://www.gosat.nies.go.jp/en/
GOSAT-2 Project http://www.gosat-2.nies.go.jp
GOSAT-GW Project https://gosat-gw.nies.go.jp/en/
>>>If you would like to use GOSAT series data, please click here (user registration is required).