Effects on Children - Chornobyl NPS Accident -
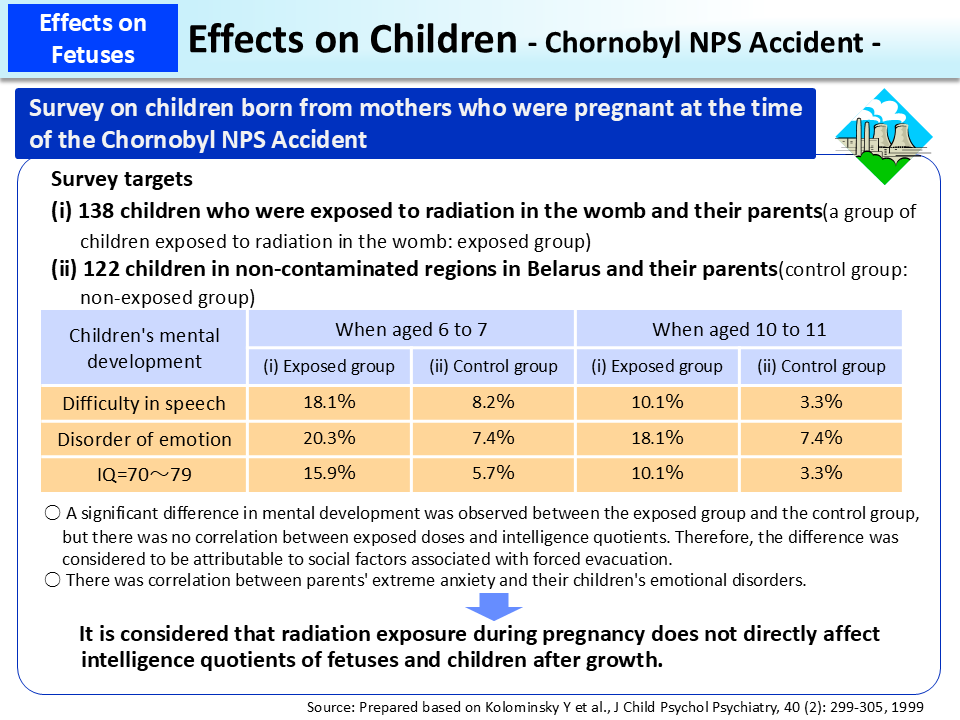
Researchers in Belarus conducted surveys targeting 138 children born from mothers who were pregnant and were residing near the nuclear power plant at the time of the Chornobyl NPS Accident and 122 children born from mothers who were pregnant at the time of the accident but were exposed to little radiation. The surveys were conducted twice when survey targets were aged 6 to 7 and when they were aged 10 to 11 in order to study effects of radiation exposure in the womb on their mental development.
In both surveys, incidences of difficulty in speech and disorder of emotion were larger among the exposed group than among non-exposed group with statistically significant differences.
Regarding intelligence quotient, fewer children in the exposed group were above the average compared with the non-exposed group and children on the borderline between normal levels and mental retardation were clearly larger in number.
However, no correlation has been found between estimated absorbed doses to the thyroid in fetal life and intelligence quotient and possibilities of other factors are suggested such as social-psychological and sociocultural factors (school education and guardians' academic levels, etc.) associated with forced evacuation from contaminated regions. The possibility that radiation exposure during pregnancy has directly affected the intelligence quotients of fetuses and children after growth is considered to be low.
A survey targeting parents using a stress evaluation index revealed clear correlation between parents' anxiety and children's emotional disorders.
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2013
- Updated on March 31, 2024