Incidence Rates of Thyroid Cancer: Overseas
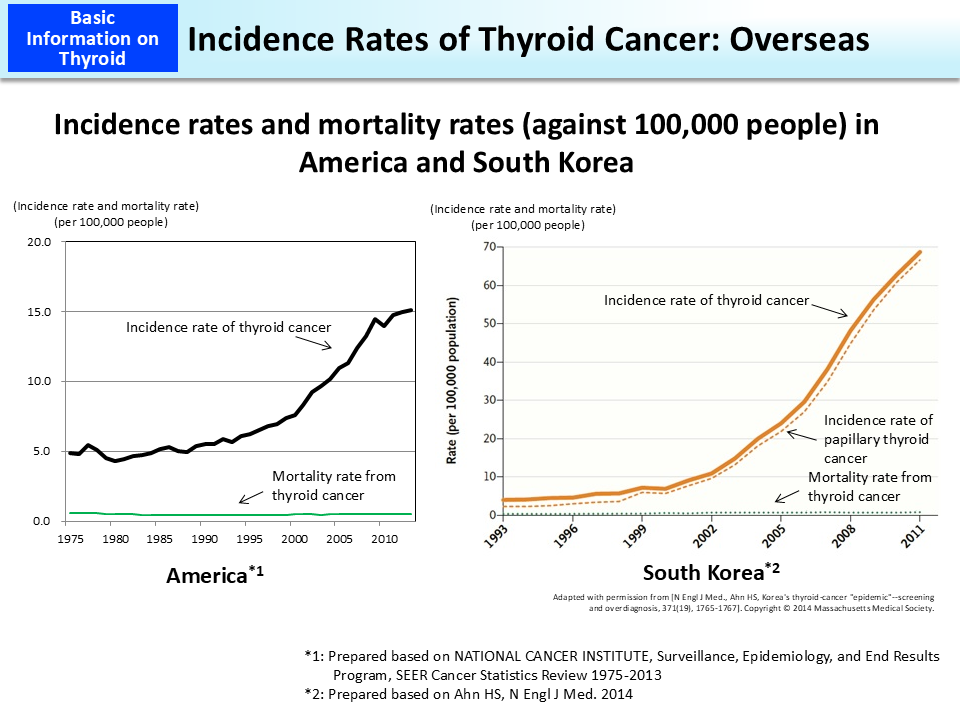
In recent years, sharp increases in the incidence rate of thyroid cancer have been reported, which is said to be due to increases in the frequencies of medical surveys and use of healthcare services as well as the introduction of new diagnostic technologies, resulting in detection of many cases of micro thyroid cancer (micro papillary carcinoma).
As the mortality rate has remained almost unchanged despite sharp increases in the incidence rate, the possibility of overdiagnoses (detection of many cases of non-fatal micro papillary carcinoma that have no symptoms) is pointed out.1
Increases in the incidence rate of thyroid cancer are global trends observed in such countries as America, Australia, France and Italy, but are especially notable in South Korea. In South Korea, official assistance for thyroid cancer screening was commenced in 1999 to enable people to receive the most-advanced screening at low cost. This is considered to have prompted a larger number of people to receive screening, leading to significant increases in the incidence rate of thyroid cancer.
- International Agency for Research on Cancer “Overdiagnosis is a major driver of the thyroid cancer epidemic: up to 50–90% of thyroid cancers in women in high-income countries estimated to be overdiagnoses” (August 18,2016)
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2017
- Updated on March 31, 2019