- MOE
- National Parks of Japan
- Definition of National Parks
- Purpose and Function
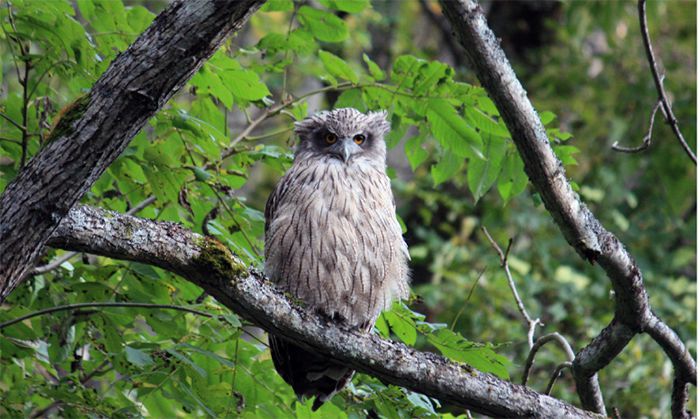

National parks aim to protect Japan's exceptional natural sites and preserve them for future generations so the latter can experience these with the same sense of wonder and joy as our generation.
To achieve these objectives, national parks are designated, protected and managed by the government under the Natural Parks Act.
Japan's Beautiful Nature as a National Treasure
Coming in contact with nature can be a deeply moving experience and yield a sense of peace. National parks, in particular, not only contain beautiful natural landscapes but also abound in wildlife and cultural history. A distinctive feature of Japan's national parks is that they include a diverse range of natural environments such as forests, agricultural land and small villages. While they offer opportunities to explore natural sites that have remained virtually intact over the years, they also contain scenic spots that blend traditional lifestyles with the surrounding natural environment, allowing visitors to experience Japanese history and culture.
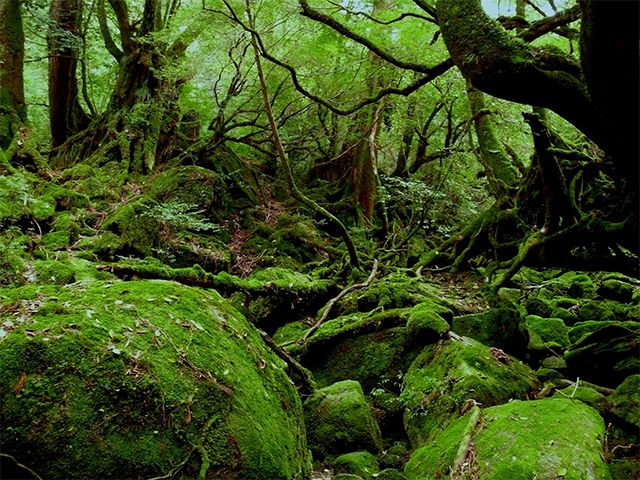
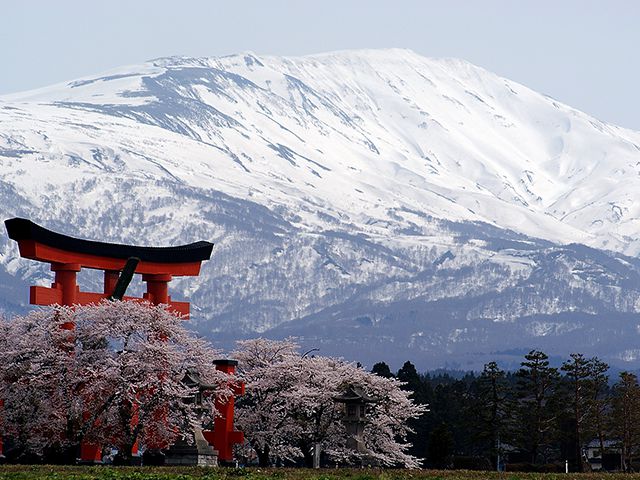


Japan's national parks serve an important function, which is to preserve Japan's unrivaled natural beauty for future generations as a national treasure. For this reason, please visit the national parks with an attitude that seeks to protect and preserve the natural environment, and fully enjoy Japan's beautiful natural environment and its changes through the different seasons.
Characteristics of Japan's National Parks
Japan is a small yet densely populated country, and its land has therefore been managed and used for various purposes since ancient times. Unlike in countries such as the Unites States or Australia, it is difficult to exclusively designate land for national park use. For this reason, Japan has adopted a Regional Natural Park System that designates national park land as such regardless of private land ownership. This means a large number of national parks include private property. Many people live in areas belonging to national parks, which are home to several industries including agriculture and forestry.
Accordingly, the national parks are managed while taking into account the lifestyles of local residents and relevant industry conditions. The presence of many stakeholders in terms of protection and use of the natural environment has increased the importance of a cooperative management and operation model that relies on collaboration among a wide range of parties.

privately owned
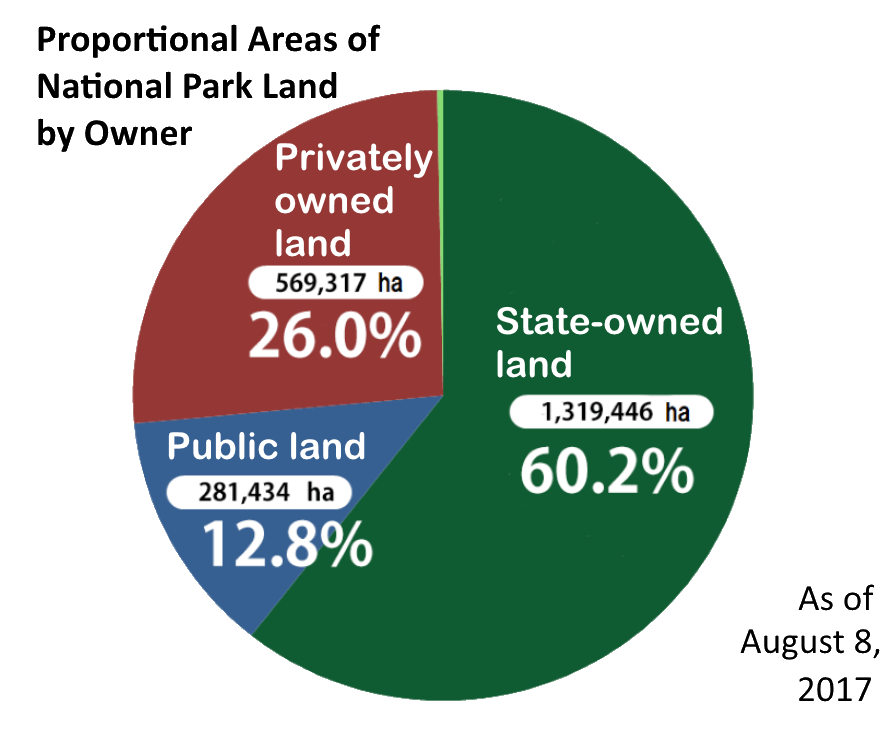
national forests under the jurisdiction of
the Forestry Agency.
Landscape Protection and Biodiversity
The protection under the Natural Park Acts mainly applies to natural landscapes, and the expression "landscapes that can be felt" does not only refer to visual perception but also includes appreciation through the five senses. By adopting a comprehensive definition of nature, the Natural Parks Act has contributed substantially to the preservation of the natural environment and biodiversity.

Yakushima Deer

Eagle Resting on Drift Ice
In Japan, national parks make up the largest designated land area subject to a system of natural environment preservation. They serve as a platform for national biodiversity, broadly encompassing natural vegetation in remote mountain areas at high elevations, as well as distribution areas for large mammals and for animals and plants that are endemic to mountainous areas.
Coming in Contact with Nature
National parks also serve as locations where people can come into contact with nature for the purpose of deepening their knowledge about nature, improving their health or taking part in recreational activities. They offer a variety of opportunities to experience nature including mountain climbing, hiking, skiing, camping, canoeing, snorkeling, bird watching, and observation of nature. To encourage people to participate in these activities, national parks feature visitor centers, hiking trails, information signboards and other facilities, as well as nature observation groups.

Diving Enthusiasts

Mountain Climbers at Mt. Shirouma


