Ensuring Safety for Temporary Storage of Designated Waste
Designated waste includes ash left after incinerating waste contaminated with radioactive materials, sludge generated through sewage treatment, soil that remains at purification plants to supply tap water (p.31 of Vol. 2, "Waterworks System"), agricultural by-products such as rice straw and pasture grass, etc.
As of September 30, 2017, there was a total of over 200,000 tons of designated waste in 11 prefectures including Tokyo Metropolis. Such waste is temporarily being stored at incineration facilities, purification plants, sewage treatment facilities, farmland, etc., where it was generated, until the national government establishes a proper disposal system.
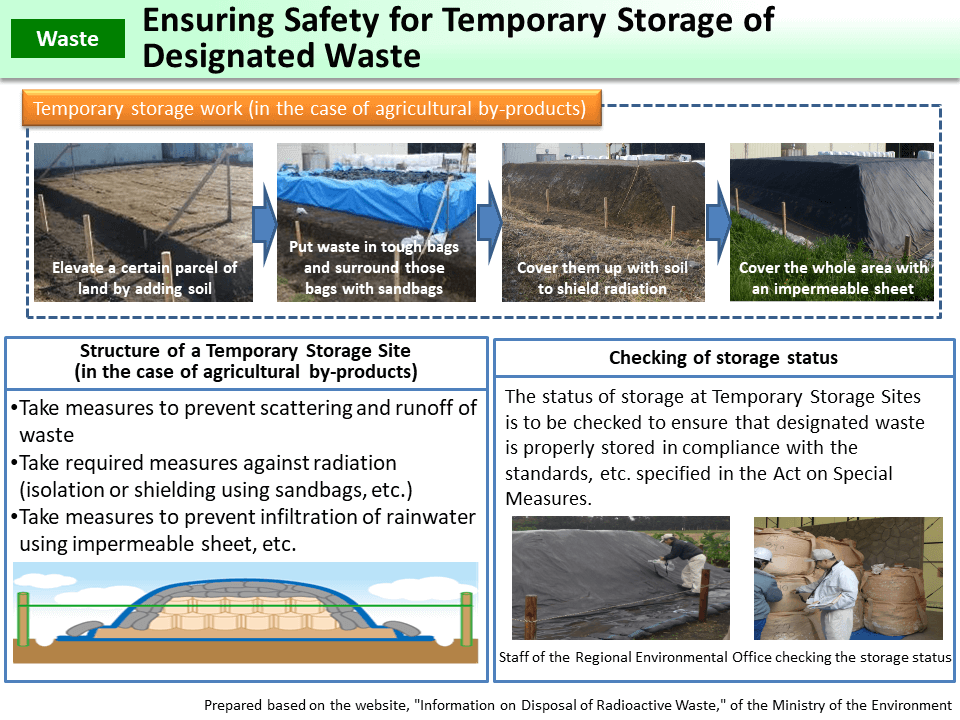
The waste is to be covered with impermeable sheets, etc. to prevent infiltration of rainwater and measures to prevent scattering and runoff of the waste are supposed to be taken voluntarily in line with the guidelines and the Act on Special Measures Concerning the Handling of Environment Pollution by Radioactive Materials. Officials of the Ministry of the Environment visit various locations and check the status of temporary storage periodically to ensure safe and proper storage of designated waste.
- Included in this reference material on January 18, 2016
- Updated on February 28, 2018