Ionization due to Radiation
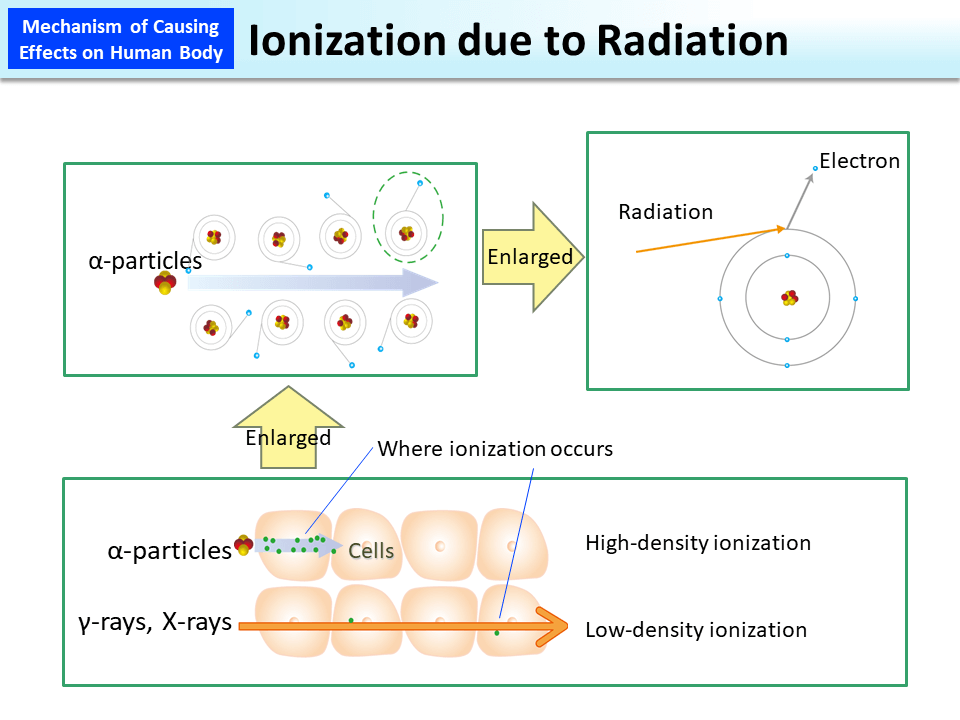
Radiation provides energy to substances along its pathway. Electrons of substances along the pathway are ejected with the given energy. This is ionization.
The density of energy provided by radiation differs by the type of radiation. Compared with β-particles and γ-rays, α-particles provide energy more intensively to substances in an extremely small area. Due to such difference in the ionization density, damage to cells differs even with the same absorbed dose.
The process in which radiation directly damages biomolecules is called direct action. As approximately two-thirds of a cell consists of water, radiation also causes the ionization of water. Radical components, which are created through the ionization and facilitate chemical reactions, damage biomolecules. This process is called indirect action (p.83 of Vol. 1, "DNA→Cells→Human Body").
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2013
- Updated on March 31, 2015