Additional Exposure Doses after an Accident (Example of Calculation)
The ambient dose rate measured with a survey meter includes γ-rays from nature. To calculate the amount of radiation released due to the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO)'s Fukushima Daiichi NPS alone, the values measured before the accident (background values) must be subtracted from the currently measured ambient dose rates to ascertain the increase caused by the accident. The values before the accident are available on the website, "Environmental Radioactivity and Radiation in Japan" (http://www.kankyo-hoshano.go.jp, in Japanese).
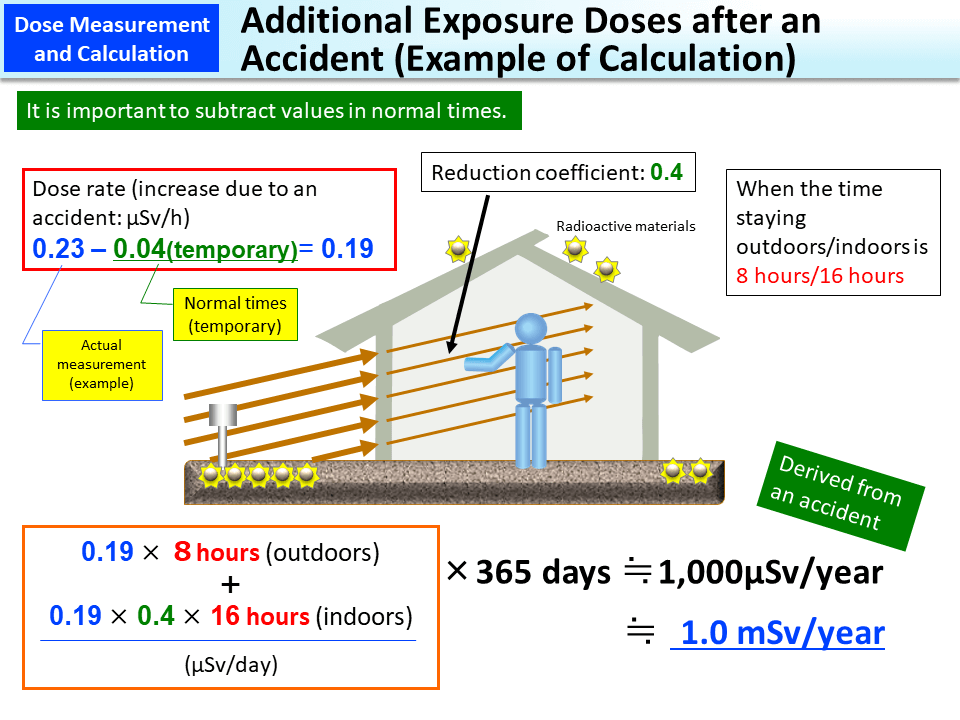
The value obtained by multiplying the increased indoor and outdoor ambient dose rates thus found by the time spent indoors and outdoors is an approximate increase in exposure dose compared with normal times (additional exposure dose).
The calculation example above for obtaining additional exposure doses after the accident is under the assumption that a person stays outdoors for eight hours and stays in a traditional Japanese house with a reduction coefficient of 0.4 for 16 hours. A daily additional exposure dose is calculated in this manner and an annual additional exposure dose is further estimated by multiplying it by 365, the number of days in a year.
An ambient dose rate of 0.23 μSv/h, which is the threshold for carrying out decontamination, is derived from an annual additional exposure dose of 1mSv (hourly exposure dose of 0.19 μSv, which will become 1 mSv in annualized terms under the same assumption on the safe side as applied in the calculation example above, plus 0.04 μSv (exposure dose due to natural radiation)).
This calculation example is for external exposure and is rather conservative without considering physical attenuation of radioactive materials and weathering effects due to transfer of radioactive materials by wind and rain, etc.
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2013
- Updated on February 28, 2018