International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
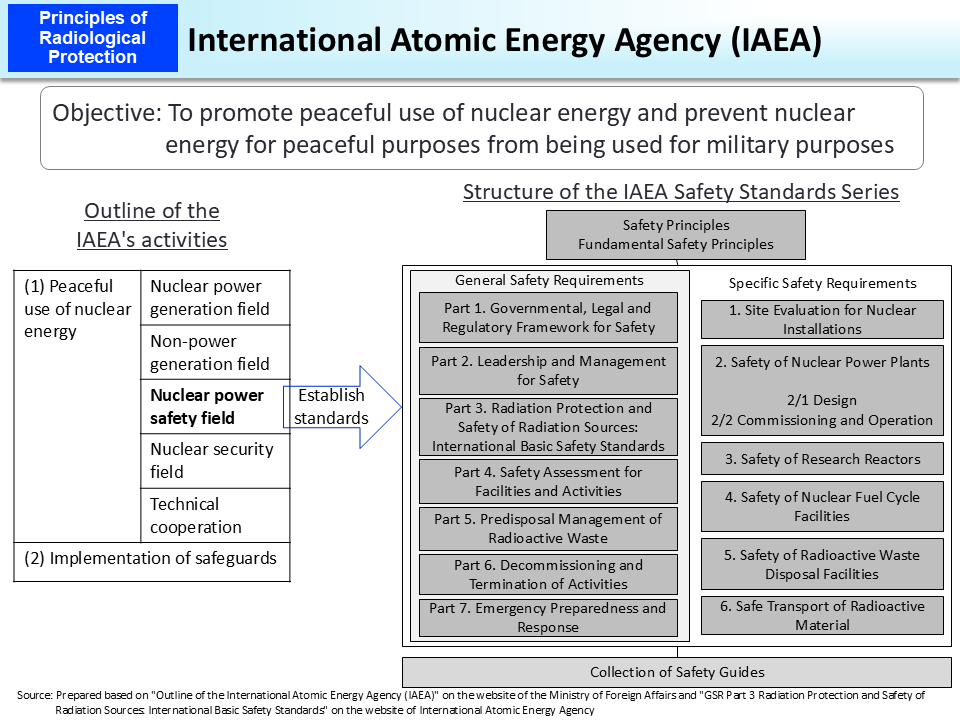
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was established in 1957 with the objective of promoting peaceful use of nuclear energy and preventing nuclear energy for peaceful purposes from being used for military purposes. The IAEA consists of 178 member countries including Japan (as of September 2023) and its major activities are roughly divided into two: the promotion of peaceful use of nuclear energy and the implementation of safeguards.
In the field of nuclear safety for peaceful use of nuclear power, the IAEA is authorized to establish safety standards as an international organization for the purpose of protecting good health and minimizing risks to the lives and property of all people, and has been contributing to the establishment and dissemination of various international safety standards and guides. The IAEA's safety standards and guides are comprised of three layers: Fundamentals, Requirements, and Guides. In particular, the Basic Safety Standards (BSS) categorized in the Requirements have been used as the guidelines and the basic numerical standards by individual countries for incorporating them in their domestic laws. The Basic Safety Standards (BSS) reflect the details of the ICPR recommendations, knowledge compiled by the UNSCEAR, and IAEA Guides, etc. and are formulated jointly by experts dispatched from IAEA member countries and relevant organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), the International Labour Organization (ILO), the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) within the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD/NEA), etc.
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2024