Health & Chemicals
FY2020 Results on Background Monitoring for Mercury in Atmosphere and Precipitation, and other Elements in Aerosols
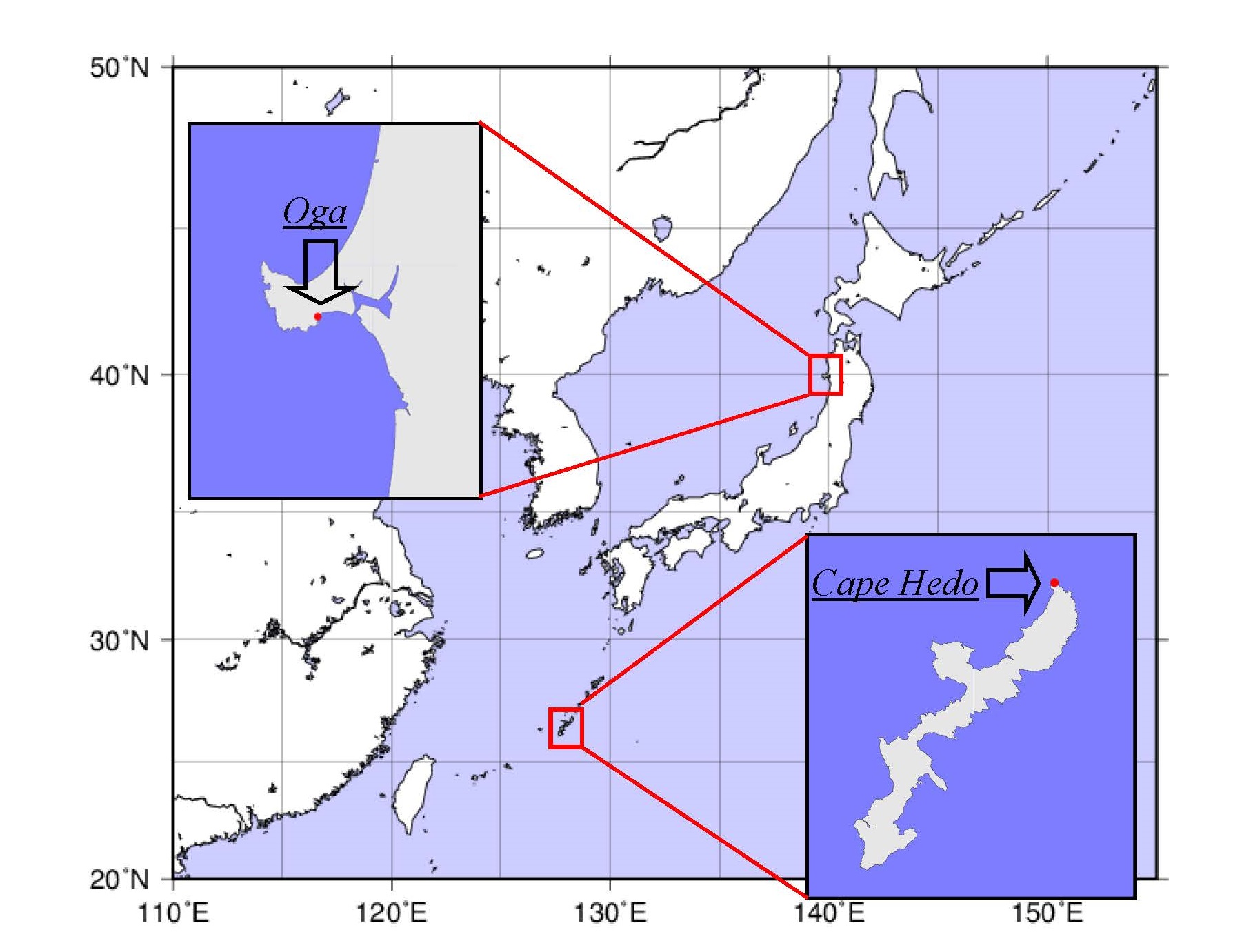
Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan (MOEJ) has been conducting background monitoring for atmospheric mercury as well as other elements in aerosols at Cape Hedo in Okinawa Prefecture (hereinafter referred to as Cape Hedo), and atmospheric mercury at Oga Peninsula in Akita Prefecture (hereinafter referred to as Oga), where direct effect from local emission sources is minimal. The results of these surveys are expected to contribute to the global mercury management.
The results of the survey in Fiscal Year (FY) 2020 (April 1, 2020 through March 31, 2021) showed that mercury concentrations in atmosphere and precipitation at Cape Hedo and Oga were well below the national guideline values, and these values did not deviate significantly from those of the past survey results.
The values of other elements in aerosols at Cape Hedo also did not significantly deviate from the past monitoring results and were well below the guideline values.
1. Overview of the Survey
MOEJ has been monitoring background concentrations of atmospheric mercury, namely Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM), Gaseous Oxidized Mercury (GOM), and Particle Bound Mercury (PBM), and mercury deposited with precipitation at Cape Hedo and Oga where the direct effect from local emission sources is minimal.
In this monitoring survey, 17 hazardous elements and six index elements have been monitored at Cape Hedo to understand the source, fate and transportation of atmospheric mercury.
2. Summary of Survey Result
(1) Atmospheric Mercury Concentration
Annual mean concentrations of the sum of all mercury forms in the atmosphere were 1.7 ng/m3 at Cape Hedo and 1.6 ng/m3 at Oga, both of which were well below the guideline values for hazardous air pollutants to reduce health risks (i.e. 40 ng/m3 as annual mean value).
Mercury in the atmosphere is mostly composed of GEM, and the average percentage of GOM and PBM were less than 1% at both sites (see Tables 4 and 6 in the Attached Document).
Annual mean concentrations of GEM and total atmospheric mercury have remained at a constant level since FY2013 at Cape Hedo (see Table 1 and the Attached Document Table 5 for detail).
Table 1 Atmospheric mercury concentrations at Cape Hedo (annual mean)
(Unit: ng/m3) [1]
|
Measured |
FY2011 | FY2012 |
FY2013 |
FY2014 |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
FY2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GEM |
2.1 |
2.0 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
|
GOM |
0.002 |
0.001 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.001 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
|
PBM |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.004 |
0.004 |
0.002 |
0.003 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
0.002 |
|
Total |
2.1 |
2.0 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
[1] The concentrations of mercury and its compounds converted to the amount of mercury are shown. The same applies to Tables 2 and 3.
Annual mean mercury concentrations of GEM and GOM have remained at a constant level since FY2014; however, concentration of PBM of FY2020 was slightly higher than in previous years at Oga (see Table 2 and Attached Document Table 7 for detail).
Table 2 Atmospheric mercury concentration at Oga (annual mean)
(Unit: ng/m3)
| Measured item | FY2014 | FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
FY2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GEM |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.5 |
1.6 |
|
GOM |
0.002 |
0.003 |
0002 |
0.003 |
0.003 |
0.002 |
0.003 |
|
PBM |
0.009 |
0.009 |
0.011 |
0.009 |
0.008 |
0.006 |
0.012 |
|
Total |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.5 |
1.6 |
Note: FY2014 monitoring program started from August 8, 2014.
(2) Mercury Concentration in Precipitation
The annual mean mercury concentration in precipitation was 5.0 ng/L at Cape Hedo and 7.9 ng/L at Oga. The FY2020 concentration at Cape Hedo was within the range of previous years. However, concentration at Oga was slightly higher than that of previous years (see Table 3 and Attached Document Tables 9 and 11 for detail).
Table 3 Mercury concentration in precipitation at Cape Hedo and Oga (annual mean)
(Unit: ng/L)
| Monitoring site | FY2016 | FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
FY2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cape Hedo |
6.6 |
4.8 |
3.9 |
5.6 |
5.0 |
|
Oga |
6.3 |
5.7 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
7.9 |
(3) Metal Element Concentrations in Aerosols Excluding Mercury
In FY2020, the annual mean concentrations of chromium, manganese, nickel, arsenic, cadmium, and lead in aerosols at Cape Hedo were 4.3 ng/m3, 4.2 ng/m3, 1.0 ng/m3, 0.61 ng/m3, 0.067 ng/m3, and 1.8 ng/m3, respectively (see Table 4). The annual mean concentration of substances were significantly below the guideline values for hazardous air pollutants to reduce health risks, where applicable (guideline values as annual mean: manganese 140 ng/m3, nickel 25 ng/m3, arsenic 6 ng/m3).
The annual mean concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, and lead were lowest compared to the previous surveys. On the other hand, the annual mean concentration of chromium was the highest compared to the previous surveys.
Table 4 Metal element concentrations in aerosols at Cape Hedo (annual mean)
(Unit: ng/m3) [2]
|
Measured item |
Guide-line |
FY2011 |
FY2012 |
FY2013 |
FY2014 |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
FY2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Chromium |
- |
0.87 |
1.3 |
1.2 |
1.4 |
0.69 |
0.65 |
0.91 |
1.8 |
2.1 |
4.3 |
|
Manganese (Mn) |
140 |
4.6 |
7.4 |
4.9 |
6.6 |
3.7 |
2.9 |
4.0 |
4.9 |
3.7 |
4.2 |
|
Nickel |
25 |
0.99 |
1.1 |
1.8 |
1.5 |
1.1 |
0.74 |
0.98 |
0.97 |
0.86 |
1.0 |
|
Arsenic |
6 |
0.76 |
0.99 |
0.98 |
1.1 |
0.74 |
0.73 |
0.73 |
0.70 |
0.66 |
0.61 |
|
Cadmium |
- |
0.12 |
0.17 |
0.19 |
0.20 |
0.13 |
0.13 |
0.11 |
0.096 |
0.083 |
0.067 |
|
Lead |
- |
5.0 |
7.3 |
6.9 |
6.5 |
3.4 |
3.1 |
2.9 |
2.7 |
2.1 |
1.8 |
[2] The concentrations of each metal and its compounds converted to the amount of each metal are shown.
Note: "guideline value" denotes the "guideline values for hazardous air pollutants to reduce health risks" of Japan.
3. Future Action
The results obtained through this monitoring are meaningful as a basis of understanding the behavior and status of atmospheric mercury in Asia-Pacific region and also in evaluating the effectiveness of the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Therefore, the MOEJ will continue to conduct monitoring and to widely provide data and report on the results.
Appendix 1 Outline of monitoring sites
Table Outline of monitoring sites
|
Site |
Cape Hedo Atmosphere and Aerosol Monitoring Station:CHAAMS |
|---|---|
|
Address |
Naganehara 1000, Ginama, Kunigami-son, Kunigami-gun, Okinawa |
|
Location |
26.87°N, 128.26°E |
|
Overview |
CHAAMS is the monitoring station established and operated by the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan, for aerosols and gases monitoring in the atmosphere in order to understand transboundary air pollution. It is located in the north end of the Okinawa island, where no anthropogenic pollution source of hazardous metals is expected in the surrounding area. Cape Hedo is the optimum location in Japan to monitor the atmospheric conditions in East Asia, as air masses from Japan, Korea, China, and Southeast Asia can be sampled depending on the season. |
|
Site |
Oga Peninsula |
|---|---|
|
Address |
Izumidai 3-2, Funagawaminato-funagawa, Oga-shi, Akita |
|
Location |
39.89°N, 139.85°E |
|
Overview |
Oga peninsula site was set up adjacently to Funakawa Ambient Air Pollution Monitoring Station operated by Akita prefecture. It is located in the south side of the Oga peninsula that protrudes into the Sea of Japan. There is no source of mercury in the surrounding area. Therefore, it is suitable for observing background mercury concentration in the northern part of Japan. |
Appendix 2 Sampling and analytical methods of different mercury forms, mercury concentration in precipitation, and other metal elements in aerosols
| Component |
Measurement items |
Sampling and analytical methods |
Site | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Atmosphere |
Mercury |
Mercury forms |
Continuous measurement with Tekran® mercury speciation system |
Cape |
|
Particulate |
17 hazardous elements |
7 days continuous sampling by using a low-volume sampler and |
Cape |
|
|
6 index elements |
||||
|
Precipitation |
Hg |
Sampling by using an automatic wet-only sampler and analyzed by CVAAS (EPA method 1631, Revision E) |
Cape |
|
Attached Documents
令和2年度 大気中水銀バックグラウンド濃度等のモニタリング調査結果について(別添)