Health & Chemicals
FY2017 Results on Background Monitoring Survey for Atmospheric Mercury and Other Metal Element Concentrations in Aerosols
The Ministry of the Environment (MOE) of Japan has been conducting a background monitoring survey for atmospheric mercury as well as other metal element concentrations in aerosols at Cape Hedo in Okinawa Prefecture (hereinafter referred to as Cape Hedo), and atmospheric mercury concentration at Oga Peninsula in Akita Prefecture (hereinafter referred to as Oga), where direct effect from local emission sources is minimal. The results of the survey may contribute to the global mercury management.
The results of the Fiscal Year (FY) 2017 (April 1, 2017 through March 31, 2018) survey showed that mercury concentrations in the atmosphere and precipitation at Cape Hedo and Oga Peninsula were well below the national guideline values, and these values did not deviate significantly from those of the previous survey results.
The values of other metal elements in aerosols at Cape Hedo also did not significantly deviate from the previous monitoring results and were well below for those having the guideline values.
1. Background Information
The MOEJ has been conducting a background monitoring survey for atmospheric mercury concentrations at Cape Hedo since FY2007 where the direct effect from local emission sources is minimal. Then, since FY2010, the monitoring results have been officially published each year after the reliability and the quality of the monitoring data were ensured.
Since August 2014, another monitoring survey at Oga has commenced.
2.Overview of the Survey
(1) Monitoring of Atmospheric Mercury Speciation, Mercury Concentration in Precipitation and Other Metal Element Concentrations in Aerosols
Mercury in the atmosphere exists in various forms such as Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM), which is the predominant form of mercury in atmosphere, Gaseous Oxidized Mercury (GOM) and Particle-Bound Mercury (PBM). It is known that the different forms of mercury behave differently in the atmosphere.
This survey aims to provide a basis on global mercury emissions, the trend of its concentrations, and the effect of mercury to the environment in Japan. The concentrations of atmospheric mercury, namely GEM, GOM and PBM, mercury deposited with precipitation, and selected metal elements other than mercury were analyzed at Cape Hedo as the national background monitoring site where the direct effect from local emission sources is minimal (see Table 1).
A monitoring survey has also been conducted at Oga (see also Table 1) in order to monitor the background concentration level in northern Japan.
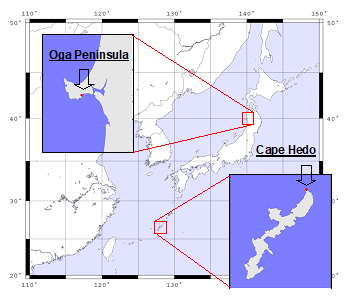
(2) Monitoring Sites (See Appendix 1 for detail)
・Cape Hedo, Okinawa Prefecture:
Cape Hedo Atmosphere and Aerosol Monitoring Station (CHAAMS), the National Institute for Environmental Studies, located in Ginama, Kunigami-son, Kunigami-gun, Okinawa
・Oga Peninsula, Akita Prefecture:
Adjacent to the Funakawa Ambient Air Pollution Monitoring Station, located in Izumidai, Funagawaminato-funagawa, Oga-shi, Akita
(3) Monitoring Methods, Survey Items and Monitoring Frequency (See Appendix 2 for detail)
The atmospheric monitoring was conducted by using a continuous mercury speciation analyzer. The precipitation was collected by the wet-only sampler, and the mercury concentration was analyzed based on the method specified by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
| Category | Survey item | Monitoring frequency | Monitoring site |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric mercury component | Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) | Continuous (16 times/day) | Cape Hedo, Oga |
| Gaseous Oxidized Mercury (GOM) | Continuous (8 times/day) | ||
| Particle-Bound Mercury (PBM) | |||
| Other metal elements in aerosols (17 hazardous elements and 6 index elements) | Weekly (7-day continuous sampling) | Cape Hedo | |
| Precipitation components | Mercury concentration in precipitation | Weekly (7-day continuous sampling) | Cape Hedo, Oga |
Note 1: "Gaseous Elemental Mercury" in this survey refers to the elemental mercury existing in the air (Hg0). "Gaseous Oxidized Mercury" refers to the oxidized mercury (Hg2+) in gaseous form, and "Particle-Bound Mercury" is mercury suspended or bound to floating particles in the atmosphere.
Note 2: The monitoring method of this survey is different from that of the harmful air pollutant monitoring survey conducted under the Air Pollution Control Act. (refer to Annex)
3. Summary of Survey Result
(1) Atmospheric Mercury Concentration
Annual mean concentrations of the sum of all mercury forms in the atmosphere were 1.6ngHg/m3 at Cape Hedo, and 1.6 ngHg/m3 at Oga, both of which were well below the guideline value for reduction of health risk by harmful air pollutants (i.e. annual mean value 40 ngHg/ m3).
Mercury in the atmosphere is mostly composed of GEM, and the average percentage of GOM and PBM were less than 1% at both sites (see Table 3 and 6 in the Annex).
While annual mercury concentrations of both total and each mercury form at Cape Hedo have remained largely unchanged (see Table 2 and Table 4 in the Annex for detail).
Table 2 Atmospheric mercury concentrations at Cape Hedo by fiscal year (annual mean)
| Measured item | FY2007 | FY2008 | FY2009 | FY2010 | FY2011 | FY2012 | FY2013 | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 | FY2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaseous Elemental Mercury | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| Gaseous Oxidized Mercury | - | - | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Particle-Bound Mercury | - | - | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| Total | - | - | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
Note: The FY2007 mean value is calculated from the data starting on 16 October when the monitoring program began. The annual mean obtained using the total concentration with oxidized mercury, and particle-bound mercury is calculated from the data in October 2009 and onward when stable monitoring was established.
Annual mercury concentrations of both the total and each mercury form at Oga have remained at virtually similar level as the values from FY2016 (see Table 3 and Table 7 in the Annex for further detail)
Table 3 Atmospheric mercury concentration at Oga (annual mean)
| Measured item | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 | FY2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) |
1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Gaseous Oxidized Mercury (GOM) |
0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Particle-Bound Mercury (PBM) |
0.009 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.009 |
| Total | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
Note: FY2014 values were calculated from data starting on 8 August, 2014, when the monitoring program began.
(2) Mercury Concentration in Precipitation
Annual mean mercury concentration in precipitation at Cape Hedo was 4.8ngHg/L. There are no guideline values established for mercury in precipitation, however, for reference, the result was well below the drinking water standard in Japan of 500 ngHg/L for mercury. (See Table 4 and Table 9 of the Annex for detail)
Based on the discussion at "the expert committee for hazardous metal monitoring survey" of FY2015 and the results of comparative test for one year, an improved analytical procedure for measuring mercury concentration in precipitation was adopted and applied from FY2016. (From the results of one year comparative test carried out from February 2016 to February 2017, it was revealed that the measured values obtained from improved analytical procedure were approximately 1.3 to 1.4 times larger than those obtained from previous analytical procedure. (See Reference 3 in the Annex for detail)
Annual mean mercury concentration in precipitation at Oga was 5.7ngHg/L by using improved analytical procedure. For reference, the result of Oga was also well below the drinking water standard for mercury (see Table 5 and Table 11 in the Annex for detail).
Table 4 Mercury concentration in precipitation at Cape Hedo by fiscal year (annual mean)
[Improved Analytical Procedure]
| Measured item | FY2016 | FY2017 |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury concentration | 6.6 | 4.8 |
(Reference: Mercury concentration in precipitation at Cape Hedo by fiscal year (annual mean)
[Previous Analytical Procedure])
| Measured item | FY2008 | FY2009 | FY2010 | FY2011 | FY2012 | FY2013 | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury concentration | 3.4 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 4.3 |
Table 5 Mercury concentration in precipitation at Oga (annual mean)
[Improved Analytical Procedure]
| Measured item | FY2016 | FY2017 |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury concentration | 6.3 | 5.7 |
(Reference: Mercury concentration in precipitation at Oga (annual mean)
[Previous Analytical Procedure])
| Measured item | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury concentration | 2.5 | 2.9 | 4.7 |
Note: FY2014 average value was calculated from the data starting on 25 August, 2014, when the monitoring program began.
(3) Metal Element Concentration in Aerosols excluding Mercury
In this monitoring survey, 17 hazardous elements and six index elements have been monitored since FY2009 at Cape Hedo in order to understand the relationship between atmospheric mercury concentrations and other metallic element concentrations in aerosols.(See Table13, 14 and 15 in the Annex for details) Among the above elements, the results of six major metal elements (nickel, arsenic, manganese, lead, cadmium, and chromium) are shown in Table 6.
In FY2017, the annual mean concentrations of nickel, arsenic, and manganese in aerosols at Cape Hedo were 0.98ngNi/m3, 0.73ngAs/m3, and 4.0ngMn/m3, respectively, which were below the "guideline values for reduction of health risk by harmful air pollutants".
The annual average concentration of lead, cadmium and chromium, of which the "guideline values" have not been established, were 2.9 ngPb/m3, 0.11 ngCd/m3 and 0.91 ngCr/m3, respectively in FY2017.
The concentrations of lead and cadmium showed the lowest values of the whole observation period, while the concentration of arsenic is the second lowest value of the whole observation period. The concentration of nickel, manganese and chromium are slightly higher than those of the last year.
Table 6 Metal element concentrations in aerosols at Cape Hedo by fiscal year (annual mean)
| Measured item | Guideline value | FY2007 | FY2008 | FY2009 | FY2010 | FY2011 | FY2012 | FY2013 | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 | FY2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel (Ni) |
25 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.74 | 0.98 |
| Arsenic (As) |
6 | 1.4 | 0.68 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.1 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.73 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 140 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 5.5 | 4.6 | 7.4 | 4.9 | 6.6 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 4.0 |
| Lead (Pb) |
- | 12 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 5.7 | 5.0 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 3.4 | 3.1 | 2.9 |
| Cadmium (Cd) |
- | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.11 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
- | 0.83 | 0.52 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.87 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
Note:"guideline value" indicates the "guideline values for reduction of health risk by harmful air pollutants" in Japan.
4. Future Action
The results obtained through this monitoring survey are meaningful as a basis of understanding the behavior and status of atmospheric mercury in Asia-Pacific region and also in evaluating the effectiveness of the Minamata Convention on Mercury in the future. Therefore, the MOE of Japan will continue to conduct monitoring surveys and to widely provide data and report on the results.
Appendix 1 Outline of monitoring sites
| Site | Cape Hedo Atmosphere and Aerosol Monitoring Station:CHAAMS |
|---|---|
| Address | Naganehara 1000, Ginama, Kunigami-son, Kunigami-gun, Okinawa |
| Location | 26.87°N, 128.26°E |
| Overview | CHAAMS is the monitoring station established and operated by the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan,for aerosols and gases in the atmosphere in order to understand transboundary air pollution. It is located in the north end of the Okinawa island, where no anthropogenic pollution source of hazardous metals is in the surrounding area. Cape Hedo is the optimum location in Japan from which to monitor the atmospheric conditions in East Asia, as air masses from Japan, Korea, China, and Southeast Asia, can be sampled, depending on the season. |
| Site | Oga Peninsula |
|---|---|
| Address | Izumidai 3-2, Funagawaminato-funagawa, Oga-shi, Akita |
| Location | 39.89°N, 139.85°E |
| Overview | Oga peninsula site is set up adjacently to Funakawa Ambient Air Pollution Monitoring Station operated by Akita prefecture. It is located in the south side of the Oga peninsula that protrudes into Japan Sea. There is no source of mercury in surrounding area.Therefore, it is suitable for observing background mercury concentration in the northern part of Japan. |
Appendix 2 Sampling and analytical method of different mercury forms, mercury concentration in precipitation, and other metal elements in aerosols
| Component | Measurement items | Sampling and analytical methods | Site | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Mercury | Mercury forms (GEM, GOM, PBM) |
Continuous measurement with TekranR mercury speciation system | Cape Hedo, Oga |
| Particulate matter | 17 hazardous elements: Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, As, Cr, V, Ni, Se, Sb, Ba, Co, Mn, Sn, Te, Tl, Be | 7 days continuous sampling by using a low-volume sampler and analyzed by ICP/MS | Cape Hedo | |
| 6 index elements: Al, Fe, Ca, Na, Mg, K | ||||
| Precipitation | Hg | Sampling by using an automatic wet-only sampler and analyzed by CVAAS (EPA method 1631) | Cape Hedo, Oga | |
Attached Documents
・平成29年度大気中水銀バックグラウンド濃度等のモニタリング調査結果について(別添)