Definition of Sato-umi
![]()
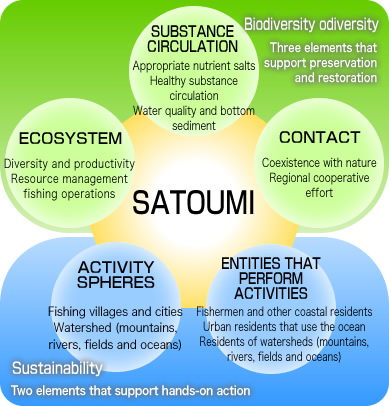
Sato-umi is a coastal area where biological productivity and biodiversity has increased through human interaction.
In Japanese, "SATO" means the area where people live, and "UMI" means the sea.
Sato-umi is an important sea-area which has been supporting culture and cultural exchanges through such things as fisheries and the distribution of products. It is an area which includes both Nature and human-beings, as well as an area in which both high biological productivity and biodiversity are expected. Healthy Sato-umi provides numerous blessings: when the material circulation function is appropriately maintained, when integrated and comprehensive management of the land and coastal area is performed, and when the rich and diversified ecosystem and natural environment are conserved. This 'preferable coastal area environment' must be maintained with the cooperation of more people in order to accede this precious environment to future generations.
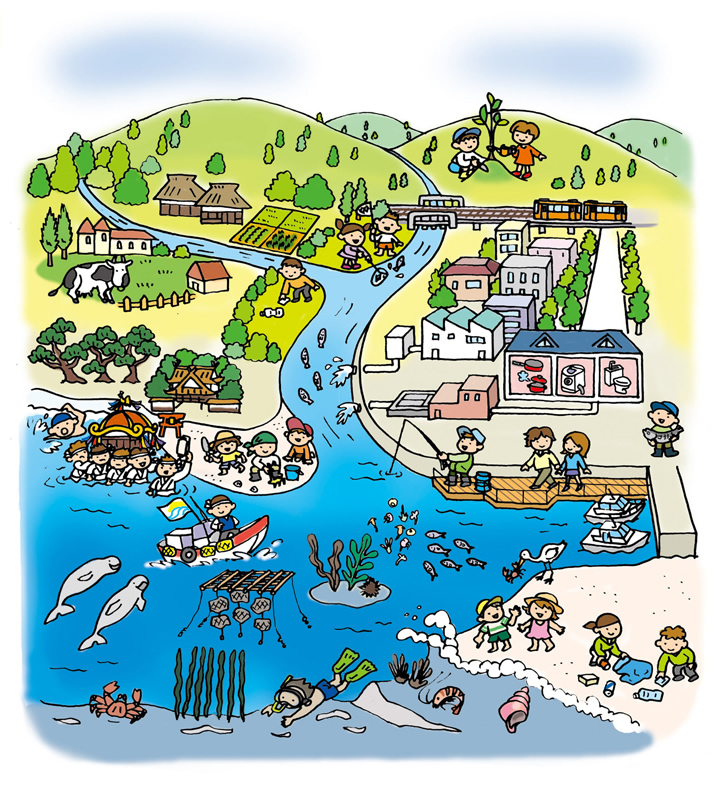
Pollutants discharged from industrial activities and the households of people living on land degrade water quality and reduce the seaweed beds, tidal flats and other areas that play an important role in water purification and also provide habitat environments for marine organisms. In response to these problems as well as the problems of increased marine litter, reduced ocean biodiversity, reduced biological populations and so on, human efforts such as reducing the pollutants that flow into the ocean from land areas, building seaweed beds and tidal flats, cleaning up coastal areas and so on can halt the?degradation of ocean environments, helping to make them good environments once more and create oceans of abundance. Another way for human beings to exercise appropriate management is to intentionally do nothing for specific ocean regions, for example by establishing "no fishing" zones, in order to keep ocean environments close to their wild state and protect ocean ecosystems. It is essential to seek ways for human beings to interact with the oceans that are appropriate for the ocean environment in each region, and to maintain this interaction on an ongoing basis.
Download:Sato-umi pamphlet (0.8MB)
Download an updated version of Acrobat Reader at Adobe Reader download.












