Save the World's Forests
prev(2/5)|Save the World's Forests|next(4/5)
2. Vital Roles of Forests
2-1. Mitigation of Climate Change risk
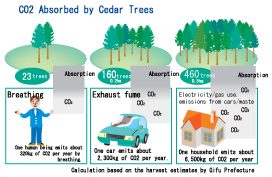 Trees store carbon absorbed through photosynthesis. As well as this storage, forests function to keep a great amount of carbon in the soil.
Trees store carbon absorbed through photosynthesis. As well as this storage, forests function to keep a great amount of carbon in the soil.
The 4th Assessment Report of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published in 2007 reveals that 20% of greenhouse gas emissions of the world have been caused by the development of forests for other purposes including agricultural use.
As the Earth heats up, considerable damage can be expected. Coastlines across the world will sink due to rising sea-levels, natural disasters will occur more frequently, and infectious diseases will spread.
- Increasing forest area to absorb more carbon
- Restricting deforestation/forest degradation to reduce carbon emissions
These two both play vital roles in mitigating climate change risk.

2-2. Conservation of Biodiversity
 Trees both tall and short, undergrowth, and many other plants grow in the forest ecosystem. Animals and insects also live there, and eat the fruits of these plants, or make their homes in the tree trunks or under the ground. A forest is a precious space rich in biological diversity.
Trees both tall and short, undergrowth, and many other plants grow in the forest ecosystem. Animals and insects also live there, and eat the fruits of these plants, or make their homes in the tree trunks or under the ground. A forest is a precious space rich in biological diversity.
Deforestation and fragmentation of vegetation could greatly affect biodiversity.
For example, among the primates, gibbons living in fragmented forests have been reported to have their range of activity limited, and therefore to have almost no communication with other neighboring groups. This means they are likely to lose breeding opportunities and suffer reduction in population. Other examples include insects like honeybees, which eat honey from the flowers and carry pollen. Their numbers and diversity are directly affected by deforestation. Once populations are reduced, it takes long time for them to recover. Woodpeckers' population density and diversity also clearly depend on the density of old trees and standing dead trees.
In this way, deforestation has implications for the loss of biodiversity.