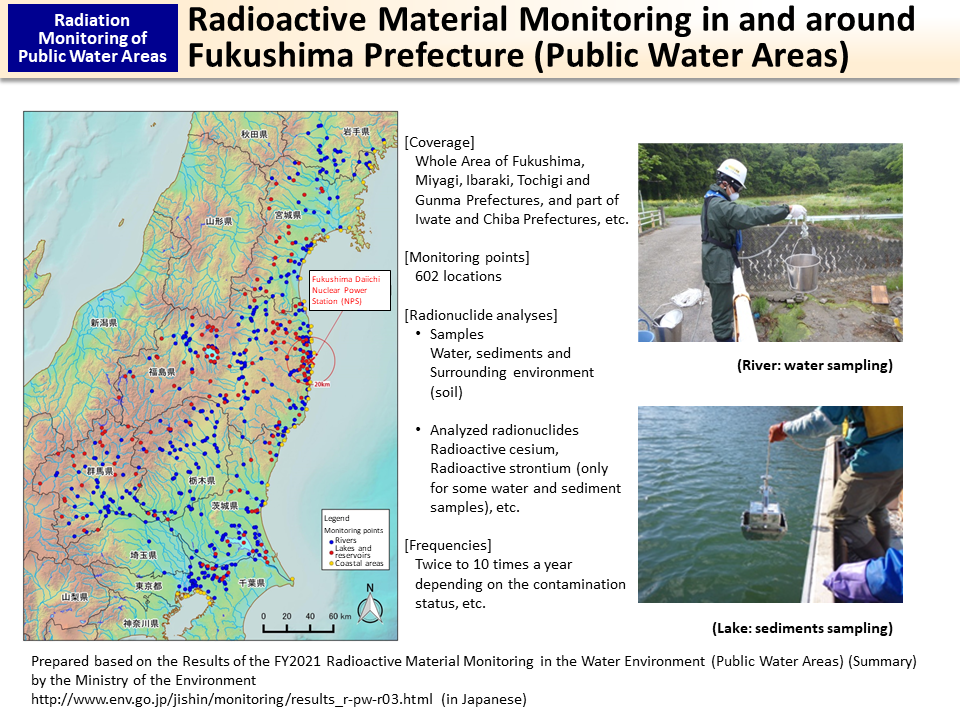
Radioactive Material Monitoring in and around Fukushima Prefecture (Public Water Areas)
Radioactive material monitoring was conducted at rivers, lakes and coastal areas in Miyagi, Ibaraki and other Prefectures, centered on Fukushima Prefecture, where contamination with radioactive materials was suspected.
In FY2021, monitoring covered 602 locations and analysis was conducted for radioactive cesium and strontium in water, etc.
Monitoring results of radioactive cesium concentrations in water are as follows. Monitoring results for sediments (mud of the bottom of rivers, lakes, etc.) are shown in p.44 of Vol. 2, “Radioactive Material Monitoring in the Water Environment (River Sediments)” through to p.46 of Vol. 2, “Radioactive Material Monitoring in the Water Environment (Coastal Area Sediments).”
[Monitoring results of radioactive cesium concentrations in water]
River water samples (2,014 samples): Radioactive cesium concentrations were all below the detection limit.
Lake/reservoir water samples (1,409 samples): Radioactive cesium concentrations were all below the detection limit except for those in 8 samples collected at 2 locations in the Hamadori District and 1 sample collected at 1 location in the Nakadori District, Fukushima Prefecture.
Coastal samples (534 samples): Radioactive cesium concentrations were all below the detection limit.
- At all locations where radioactive cesium or strontium was detected, amounts of suspended solids (SS) and turbidity were relatively large.
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2013
- Updated on March 31, 2023