The Global Desertification - The Situation, and the Challenges for Japan -
prev(4/8)|The Global Desertification|next(6/8)
4. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification
In order to address issues concerning desertification on a global scale, the ‘United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification in Countries Experiencing Serious Drought and/or Desertification, Particularly in Africa'(commonly known as the UN Convention to Combat Desertification)was adopted on June 17, 1994. This convention aims to promote cooperation among the international community towards solving the desertification problems which threaten developing countries, especially in Africa.
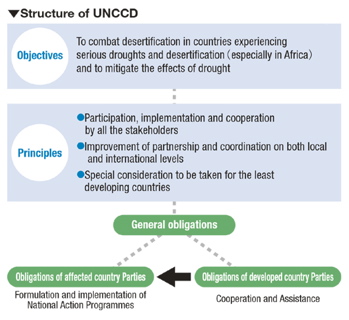
UNCCD sets out fundamental guidelines for action as its ‘principles', and focuses on the provision of financial mobilization.
The Convention obliges the affected country Parties to formulate National Action Programmes, and also obliges all the Parties to report regularly about their actions taken to combat desertification to the Conference of the Parties.
Under the Convention, the Committee on Science and Technology has been established as a subsidiary body of Conference of the Parties to provide it with advice on scientific and technical issues. The Committee for the Review of the Implementation of the Convention has been also established to review regularly the implementation of the Convention.
Subsidiary bodies of the Conference of the Parties under the Convention
1.Committee on Science and Technology(CST)
CST provides the COP with scientific and technical information and advice.
2.Committee for the Review of the Implementation of the Convention(CRIC)
CRIC was established at COP 5 in order to conduct a regular review on the implementation of
the Convention(COP 5/Decision 1).
Framework of UNCCD
(a)Definition of desertification
“Desertification” is defined as ‘land degradation in arid, semi-arid and dry subhumid areas resulting from various factors, including climatic variations and human activities'. Desert(hyper-arid areas)is outside the scope of the convention (Article 1).
(b)General obligations
Parties shall implement the obligations such as 1)adopting an integrated approach addressing the physical, biological and socio-economic aspects of the processes of desertification and drought, 2)giving due attention to the situation of affected developing country Parties with regard to economic situation, and 3)integrating strategies for poverty eradication into efforts to combat desertification and mitigate the effects of drought(Article 4).
(c)Obligations of affected country Parties
To combat desertification and mitigate the effects of drought, affected country Parties undertake to 1)allocate adequate resources, 2)establish strategies and priorities within the framework of sustainable development plans, and 3)facilitate the participation of local populations with the support of nongovernmental organizations(Article 5).
(d)Obligations of developed countries Parties
Developed country Parties undertake actively to support the efforts of affected developing country Parties to combat desertification and mitigate the effects of drought, and to provide them with substantial financial resources, while promoting the mobilization of financial resources including funding from the Global Environment Facility, and facilitating access by affected country Party, to appropriate technology, knowledge and know-how (Article 6, Article 20-2). In the provision of assistance, priority shall be given to supporting action programmes (Article 9. 2).
(e)Action programmes
Affected country Parties shall prepare and implement national action programmes (Article 9-1). National action programmes shall 1)incorporate long-term strategies to combat desertification and mitigate the effects of drought and be integrated with national policies for sustainable development, 2)give particular attention to lands that are not yet degraded or which are only slightly degraded, and 3)provide for effective participation of NGOs and local populations in policy planning, decision-making, and implementation and review of national action programmes(Article 10.2).
(f)Financial resources and financial mechanisms
The provisions about financial resources include, 1)developed country Parties, while giving priority to affected African country Parties, undertake to promote the mobilization of financial resources including funding from the Global Environment Facility(Article 20.2.(b)), and 2)Parties shall seek full use and qualitative improvement of all national, bilateral and multilateral funding sources(Article 20.4.).
As for financial mechanisms, Global Mechanism has been established in order to promote the mobilization of financial resources for affected developing country Parties(Article 21.4.). (Note: Global Mechanism is hosted by the International Fund for Agricultural Development(IFAD).)
(g)Committee on Science and Technology
As a subsidiary body of the Conference of the Parties to provide it with information
and advice on scientific and technological matters, Committee on Science and Technology has been established, consisting of government representatives competent in the relevant fields of expertise (Article 24.1.). The Conference of the Parties shall establish and maintain a roaster of independent experts nominated by the Parties(Article 24.2.).