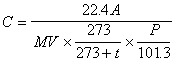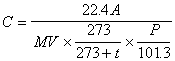Cabinet Order for Offensive Odor Control Law (abstract)
Measurement Method of Specified Offensive Odor Substances
Environment Agency Notification No.9 of 1972
Last Amended by Environment Agency Notification No.4 of 1996
The measurement method of Specified Offensive Odor Substances stipulated in the Article 5 of the Ordinance of the Offensive Odor Control Law (the Ordinance of the Prime Minister's Office No.39 of 1972) is enforced as of May 31, 1972.
The measurement methods of Specified Offensive Odor Substances stipulated in the Article 5 of the Ordinance of the Offensive Odor Control Law are listed in the following subparagraphs;
- i)
- Ammonia: The method listed in Attached 1
- ii)
- Methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide and methyl di-sulfide: The method listed in Attached 2
- iii)
- Tri-methyl amine: The method listed in Attached 3
- iv)
- Acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, iso-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso-valericaldehyde: The method listed in Attached 4
- v)
- iso-buthylalcohol: The method listed in Attached 5
- vi)
- Ethylacetate, methyl-iso-buthylketone: The method listed in Attached 6
- vii)
- Toluene, stylene and xylene: The method listed in Attached 7
- viii)
- Propionic acid, n-butyric acid, n-valeric acid and iso-valeric acid: The method listed in Attached 8
Attached Table 1
Measurement method of Ammonia
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the following manner:
- (1) Collecting solution
Five grams of boric acid is dissolved in water and diluted to 1 liter. - (2) Phenol sodium penta-cyanonitrosyl ion (III) acid solution
5 grams of phenol and 25 mg of sodium penta-syanonitrosyl ion (III) acid with 12 hydrates are dissolved in water and diluted to 500 ml (the solution must be stored in a cold, dark place. Solution older than 1 month should not be used.). - (3) Sodium hypochloride solution
Sodium hypochloride solution (effective chlorine 3 to 10 %) 60/C ml (where C is the concentration of the effective chlorine in the sodium hypochloride weighed at preparation.), 10 g of sodium hydroxide and 35.8 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate with two hydrates are dissolved in the water and diluted to 1 liter (this solution shall be prepared on usage). - (4) Standard ammonia solution
Sodium sulfate, desiccated at 130 degree Celsius, is dissolved in water and diluted to 1 liter and then diluted 50 times by the collection solution (1 ml of this solution contains ammonium ion corresponding to 2 micro liter of ammonia (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.)).
2. Equipment
The equipment used is listed as follows:
- (1) Sampling equipment
It is configured as shown in attached drawing and the following conditions shall be satisfied:- i)
- Absorption bottle, volume 200 ml, equipped with half-melted glass filtration spare (note 1), and containing 20 ml of collection solution. Two bottles can be connected in a series.
- ii)
- Suction pump able to draw air at 10 liters per minute with absorption bottle connected.
- iii)
- Gas meter able to measure a flow rate of 5 to 15 liters per minute.
- (2) Optical intensity meter
Spectral meter or opto-electric meter
(note 1) fine filter shall be used to avoid bottle receiving negative pressure.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed according to the following process:
- (1) Sample collection
Sample is collected in the collecting solution by air suction for 5 minutes at flow rate of 10 liters per minute. - (2) Preparation of sample solution for analysis
After collection is completed in the two suction bottles, the collecting solution is poured into a 50 ml scaled flask, then the bottles are washed with the collected solution and then cleansing fluid is added to the collecting solution. 10 ml of this solution is then placed in a capped tube for analysis of the sample solution. - (3) Measurement of optical absorption
Five milliliters of phenol and sodium penta-cyano nitrosyl ion (III) acid is added to the analyzing sample solution, and after mixing, 5 ml of sodium hypochloridte solution is added. After one hour of keeping the liquid temperature at 25 to 30 degrees Celsius, optical absorption is measured at the wavelength of 640 nm. Reference solution is the collecting solution processed in the same manner as the analyzing sample. - (4) Calibration curve
Zero to 40 ml of standard ammonia solutions are sampled sequentially, and are diluted to 50 ml with collecting solution, then 10 ml of the solution is placed in the capped tube. The solution is processed in the same manner as the optical absorption for analyzing solution and a calibration curve is drawn. - (5) Calculating concentration
Through the calibration curve in (4), the amount of ammonia in the analyzed sample solution is sought (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) and, using the following equation, the density of its air is calculated.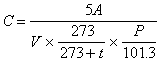
Where C is the concentration of ammonia in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the ammonia in the analyzing sample solution (unit : micro liter), V is the gas volume measured by the gas meter (unit : liter), t is temperature at gas meter (unit : degree Celsius) and Pis the atmospheric pressure at the sampling (unit : kPa).
Remarks
- In the operation of 3-(1), a lower flow rate is permitted in cases where a constant flow rate of 10 liter per minute is not achievable owing to a clogged filtration sphere or to unavoidable reasons, but the sensitivity is still high enough to conduct proper analysis.
- In cases of low water content in the sample and no sorption effect, sample gas may be collected through operation of 1-3-(2)-i) of the attached table 2 by using the equipment shown in 1-2-(1)-i) and (2) (note 2) of the attached table 2. The sample gas collected in the sampling bag shall be collected as soon as possible through operation of 1-3-(1) (note 3) by using the sampling equipment shown in 1-3-(1) (note 3).
- (note 2)
- The inner volume of the sampling bag shall be approximately 50 liter.
- (note 3)
- Lower flow rate is permitted in case where the constant flow rate of 10 liter per minute is not easily achieved.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the ammonia concentration in the exhaust gas measured by method of JIS K0099.
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Attached figure
- Suction bottle
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
Attached Table 2
Measurement method of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide and methyl di-sulfide
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
1. Reagent
The calibration gas for measurement of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide and methyl di-sulfide is prepared before use by permiation tube method or equivalent method, or method listed below. Calibration gas bottle for preparation is shown in the Fig. 1,is made of borosilicate glass, contains a piece of fluoride resin, and the volume is known. Before use, bottle shall be washed with 10N-phosphoric acid and water, and be desiccated and substituted air by nitrogen.
- (1) Calibration gas of methyl mercaptan
One milliliter of gaseous methyl melcaptan is collected with a gas syringe, and is injected through silicon rubber cap of calibration gas bottle. Leave longer than 10 minutes after mixing. - (2) Calibration gas of hydrogen sulfide
One milliliter of gaseous hydrogen sulfide is collected with a gas syringe, and is injected through silicon rubber cap of calibration gas bottle. Leave longer than 10 minutes after mixing. - (3) Methyl sulfide
Three micro liters of methyl sulfide is collected with a micro-syringe, and is injected through silicon rubber cap of calibration gas bottle. To be vaporized and leave longer than 10 minutes after mixing. - (4) Methyl di-sulfide
Three micro liters of methyl di-sulfide is collected with a micro-syringe, and is injected through silicon rubber cap of calibration gas bottle. To be vaporized and leave longer than 10 minutes after mixing.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler
One of the equipment shown below- i)
- Sampler pump with air suction power of over 10 liter per minute and the gas through portion is changeable.
- ii)
- Sampler with configuration shown in Fig. 2. (note 1)(note 2)
- iii)
- Air tight gas sampling suction bottle of volume larger than 5 liter that is shown in Fig. 3 and the sampling bag is connected inside the bottle.
- (2) Sampling bag
Made of poly-vinyl fluoride film, polyester (compound name : poly-ethylene telephthalate) film or equivalent on the storage performance, and the volume is lager than 5 liter. (note 3) - (3) Condenser tube
The configuration shown in Fig. 4 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The tube is made of borosilicate glass or fluoride resin and the inner diameter of 4 mm.
- ii)
- The tube is washed with phosphoric acid (1+4) and water, and is desiccated, then the same type of gas chromatograph filler as used for the analysis or equivalent is filled in the tube.
- iii)
- Aluminum foil is placed on the outside of the tube. It is isolated with glass fiber tape. Thermocouple is attached to measure the temperature. Nickel-chrome wire with glass fiber tube is turned on the same spacing, and fixed with glass fiber tape.
- (4) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 5 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The gas chromatograph includes flame optical detector.
- ii)
- Carrier gas path is changed at the sample inlet and is connected to contamination trap and condenser tube.
- iii)
- The molecularceive 5A or the equivalent is filled in contamination trap and is cooled by coolant of liquid oxygen or equivalent.
- iv)
- The column is made of glass or fluoride resin and the inner diameter of 3 mm and length of 3 to 5 meters. Inner side is washed with phosphoric acid (1+4) and water, and desiccated.
- v)
- The white diatomaceous earth holder of the filler is washed with acid. The filler is processed by dimethyl-dichloro silane and coated 25% with beta, beta'-oxy-di-propyonitril. Or equivalent filler is used for the purpose.
- vi)
- Temperature at the sample inlet shall be 130 degrees Celsius.
- vii)
- Temperature at the column chamber shall be 70 degrees Celsius.
- viii)
- Nitrogen is employed for carrier gas of flow of 40-50 ml per minute.
- (note 1)
- Suction case shall be made of transparent resin and is air tight structure.
- (note 2)
- Suction pump shall be with air suction power of over 10 liter per minute.
- (note 3)
- The thickness more than 35 micro meters shall be used owing to concentration change of the sample in thinner bag.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample condenser tube is heated for approximately 10 minutes at 70 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow. An analysis routine is performed on item (4) to verify no peak in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Gas sampling
According to the type of gas sampling equipment, on of the following methods is employed for gas collection to the sampling bag.- i)
- In case of 2-(1)-i), sampling pump and the sampling bag is connected with silicon rubber tube, 5 liter of sample gas is collected in the sampling bag for 6 to 30 seconds. (note 4)
- ii)
- In case of 2-(1)-ii), the sampling bag is installed in the suction case, and is connected to the fluoride resin valve. After verifying the fluoride resin valve and suction valve are opened, the suction pump connected to the suction valve is stated to operate. Approximately 5 liter of sample gas is collected in the sampling bag by depressurizing the suction case. Flow rate is adjusted by suction valve and flow rate adjustment of suction pump. The collection is performed for 6 to 30 seconds at constant flow rate.
- iii)
- In case of 2-(1)-iii), the following process is used. Open two valves of the suction bottle. Evacuate glass container by evacuation pump at the valve that is not connected to the bag (hereinafter referred as "valve A"). The evacuation pump is stopped when the sampling bag in the bottle is filled with are. Then close the valve A and connect evacuation pump to the valve that is connected to the bag (hereinafter referred as "valve B"). The air in the sampling bag is fully evacuated and the valve B is closed. Finally, by opening valve B, sample gas is introduced into the sampling bag in duration longer than 6 seconds.
- (3) Sample condensing
As shown in Fig. 6, subject component in the sampling bag is collected in the sample condenser tube for constant quantity of sample by connecting sampling bag to sample condenser tube that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen. - (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
As shown in Fig. 5, the sample condenser tube with trapped subject component, that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen, is connected to the gas chromatograph analyzer. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, and verify the stability of the flow rate and the detector sensitivity. Raise the temperature of the condenser tube to 70 degrees Celsius in approximately two minutes. Introduce subject component to the gas chromatograph. - (5) Calibration curve
Perform the same operation as item (4) for samples of calibration gases of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide and methyl di-sulfide, or diluted sample with calibration gas bottle, that are injected to the sample condenser tube that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen. The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak height of the chromatogram. - (6) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide or methyl di-sulfide in the air (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) in the condenser tube.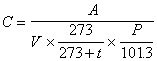
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the condenser tube (unit : micro liter), V is the gas volume collected in the condenser tube (unit : liter), t is temperature at sample condensing (unit : degree Celsius) and Pis the atmospheric pressure at the sample condensing (unit : kPa).
(note 4) Sample gas path of the sampling pump and silicon rubber tubes connecting between the sampling pump and the sampling bag shall be replaced after usage.
Remarks
- Flow ratio mixing method may be used as equivalent method of permiation method (a method that a teflon tube containing liquid gas is placed in constant temperature chamber, the low concentration gas is continuously produced by diluting liquid gas passed through the tube wall with dilution gas) for calibration gas preparation.
- Coolant for cooling condenser tube and trap tube equivalent to the liquid oxygen shall be liquid argon or material that is verified to equal to or to be higher performance of capture efficiency for sample condenser tube than liquid oxygen.
- In case of poor peak separation of gas chromatograph, optimum separation condition may be adopted such as a temperature raising of 4 degrees Celsius per minutes in the temperature range of column from 40 to 70 degrees Celsius.
- In case where the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the hydrogen sulfide concentration in the exhaust gas measured by following method.
1. Reagent
The same as shown in I-1.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler and sampling bag
The same as shown in I-2-(1)-i), ii) and (2). - (2) Condenser tube
The same as defined in I-2-(3). - (3) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The same as defined in I-2-(4).
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Gas sampling
The same operation as defined in I-3-(2)-i) and ii). - (2) Gas chromatograph analysis
- i)
- A part of the sample gas collected within 12 hours is taken with the gas syringe and directly injected to the sample inlet of the gas chromatograph analysis equipment.
- ii)
- In case where the result of procedure i) exceeds the upper detecting limit, following procedure is used. An exactly known volume of the sample gas is taken with the gas syringe, and is diluted by method of calibration bottle of I-1, the gas chromatograph analysis is performed in the manner the same as i).
- iii)
- In case where the result of procedure i) does not reach to the lower detecting limit, perform the same operation as I-3-(2) and (3).
- (3) Calibration curve
Perform the same operation as item (2) for sample of calibration gas of hydrogen sulfide, that is diluted sequentially. The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak height of the chromatogram. - (4) Calculating concentration
- i)
- In case of (2)-i) or ii), the concentration in the air is calculated by the equation of I-3-(6) by using quantity of hydrogen sulfide in the air (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) from the calibration curve of (3). Here, C is the concentration of the hydrogen sulfide in the exhaust gas (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the hydrogen sulfide (unit : micro liter), V is the gas volume collected (unit : liter), t is temperature of exhaust gas (unit : degree Celsius) and P is the pressure of exhaust gas (unit : kPa).
- ii)
- In case of (2)-iii), the same procedure defined in II-3-(6).
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 1 Calibration gas bottle
- Silicon rubber cap
- Piece of fluoride resin
Fig. 2 Gas sampling equipment
- Sampling tube
- Valve made of fluoride resin
- Sampling bag
- Suction case
- Suction valve
- Suction pump
Fig. 3 Gas sampling equipment
- Valve made of fluoride resin
- Valve made of fluoride resin
- Cramp
- Sampling bag
- Gas sampling suction bottle
Fig. 4 Condenser tube
- Silicon rubber cap
- Capillary tube
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
- Quartz glass wool
Fig. 5 Gas chromatograph analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Contamination trap
- three direction valve
- Condenser tube
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Detector
- Bypass
Fig. 6 Condensing method
or
- Sampling bag
- Condenser tube
- Fluoride resin tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
- Syringe
III. Concentration measurement in the water
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/liter)
- (2) Calibration gas
The same as defined in the First-1.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Sampling bottle
Glass bottle with teflon packing cap or capped glass bottle, volume from 500 ml to l liter. - (2) Whole pipet
Made of glass and volume of 50 ml. - (3) pH meter
- (4) Liquid syringe
Made of resin and with suitable volume (1-5 ml). - (5) Vial
Volume of 100 ml (for injection purpose) and air tight with rubber cap. - (6) Teflon film (Quad-fluoro ethylene resin film)
Quad-fluoro ethylene resin film with thickness of 0.05mm, with the size that prevents the rubber cap to touch to the sample in case of inserting between rubber cap and vial. (note 5) - (7) Aluminum cap
Fixing vial and rubber cap. - (8) Aluminum cap fixing tool
Aluminum cap is deformed to fix the cap to the vial. - (9) Constant temperature water chamber
Maintain water temperature at 30 degrees Celsius plus or minus 0.2 degree. - (10) Micro syringe (for gas use)
With suitable volume from 20 to 1000 micro liter (note 6). - (11) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The same as defined in I-2-(4)
- (note 5)
- Teflon film is not required in case of using vial rubber cap with performance equivalent to using teflon film.
- (note 6)
- Clean with nitrogen and verify no peak appears at position of subject component.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Pour 50 ml of water into a vial. Perform analysis in the procedure (3). Verify no peak appears in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Water sampling
Collecting the sample water into the sampling bottle, fill with water avoiding bubble formation and seal with cap (note 7). - (3) Head space test
- i)
- Taking 50 ml of sample water to glass container (note 8), find the required hydrochloric acid quantity to adjust pH value of 3.0 to 4.0.
- ii)
- Another 50 ml of sample water is taken to the vial with whole pipet (note 9).
- iii)
- Inject the hydrochloric acid of the quantity that is found in i) quietly in the vial (note 10).
- iv)
- Place the teflon film on vial. Seal the vial with rubber cap. Place aluminum cap on the rubber cap, fix the vial and rubber cap with aluminum cap deformed by the aluminum cap fixing tool.
- v)
- Vibrate the vial up and down by hand for approximately 30 seconds.
- vi)
- Install the vial in the constant temperature water chamber of 30 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes.
- vii)
- The constant volume (0.2 to 1 ml) of gas from the vial is taken with micro syringe through vial. Directly inject to gas chromatograph inlet for analysis.
- viii)
- Measure the pH value of the solution left in the vial by removing rubber cap of the vial. In case of pH value out of the range of 3.0-4.0, the measurement is decided to be ineffective and repeat the operation from i) to vii).
- (4) Calibration curve
Perform the same operation as item (4) for samples of calibration gases of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide and methyl di-sulfide, or diluted sample with calibration gas bottle, that are diluted sequentially and injected to the inlet of the gas chromatograph inlet. The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak height of the chromatogram. - (5) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the water is calculated by following equation by using quantity of methyl mercaptan, hydrogen sulfide, methyl sulfide or methyl di-sulfide in the vapor phase by the calibration curve of (4).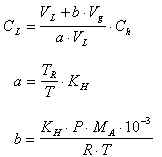
where CL is the concentration of the subject component in the water (unit : mg/liter), Ch is the concentration of the subject component in the vapor phase (unit : ppm), VL is volume of the liquid (unit : liter), Vg is volume of the liquid (unit : liter, "full volume"-"liquid volume"), Ta is the room temperature at the time of sample injected to the vial (unit : K), KH is a equivalent value of Henry's constant (unit : liter/kg, shown in the following table), MA is molecular weight (unit : g/mol, shown in the following table), T is the temperature of the chamber (unit : K), P is the atmospheric pressure (unit : kPa), Ris the gas constant (8.31 kPa liter/mol K).
Material KH MA Methyl mercaptan 83.1 48.11 Hydrogen sulfide 322.0 34.08 Methyl sulfide 38.0 62.14 Methyl di-sulfide 18.4 94.20
- (note 7)
- Store at dark place of temperature of 0 to 5 degrees Celsius. As the subject component is easily vaporized, the analysis shall be performed as soon as possible.
- (note 8)
- The sampling bottle shall be sealed immediately to store back to the dark place of temperature of 0 to 5 degrees Celsius.
- (note 9)
- Whole pipets and vials shall be cooled at temperature of 0 to 5 degrees Celsius.
- (note 10)
- Teflon film and vial rubber cap are placed on the vial, then insert the syringe.
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Attached Table 3
Measurement method of Tri-methyl amine
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Reagent decomposition
500 grams of potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water and diluted to 1 liter. - (2) Standard solution of Tri-methyl amine
Solution that is diluted tri-methyl amine solution (20-40%) by 20 times with water. The concentration of the tri-methyl amine is measured by titration with 0.1N-hydrochloric acid, employing an indication reagent of 0.1% ethyl alcohol solution of bromocresol green and 0.1% ethyl alcohol solution of methylred, with volume ratio of five to one. - (3) Ethyl alcohol
No peak shall appear in the holding time of tri-methyl amine, when it is injected in gas chromatograph. - (4) Collecting solution
Sulfuric acid diluted with water by 360 times.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Sampler and sampling bag
The equipment defined in I-2-(1) in the attached table 1. - (2) Condenser tube
The configuration shown in Fig.. 2 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The tube is made of borosilicate glass and the inner diameter of 4 mm.
- ii)
- The tube is washed with potassium hydroxide (100 g/liter) and water, and is desiccated, then the same type of gas chromatograph filler as used for the analysis or equivalent is filled in the tube.
- iii)
- Aluminum foil is placed on the outside of the tube. It is isolated with glass fiber tape. Thermocouple is attached to measure the temperature. Nickel-chrome wire with glass fiber tube is turned on the same spacing, and fixed with glass fiber tape.
- (3) Sample decomposition and condenser equipment
- i)
- The molecularceive 5A or the equivalent is filled in contamination trap and is cooled by coolant of liquid oxygen or equivalent.
- ii)
- Twenty milliliter of Decomposition reagent is poured in the decomposition bottle, and the air is substituted by nitrogen.
- iii)
- In case where the condenser tube is clogged with water in short time, the desiccate tube filled with potassium hydroxide is connected to the decomposition bottle.
- (4) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig.. 5 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The gas chromatograph includes hydrogen flame ion detector.
- ii)
- Carrier gas path is changed at the sample inlet and is connected to contamination trap and condenser tube.
- iii)
- The molecularceive 5A or the equivalent is filled in contamination trap and is cooled by coolant of liquid oxygen or equivalent.
- iv)
- The column is made of glass or fluoride resin and the inner diameter of 3 mm and length of 3 to 5 meters. Inner side is washed with potassium hydroxide and water, and desiccated.
- v)
- The white diatomaceous earth holder of the filler with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter is coated with 15% of di-glycerol, 15% of tetra-ethylene pentamine and 2% of potassium hydroxide. Or equivalent filler is used for the purpose.
- vi)
- Temperature at the sample inlet shall be 130 degrees Celsius.
- vii)
- Temperature at the column chamber shall be 70 degrees Celsius.
- viii)
- Nitrogen is employed for carrier gas of flow of 40-50 ml per minute.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample condenser tube is heated for approximately 10 minutes at 70 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow. An analysis routine is performed on item (4) to verify no peak in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Sampling
The same operation defined in I-3-(1) of the attached table 1. - (3) Sample decomposition and condensing
- i)
- After collection is finished, collecting solution in two collection bottles and that is washed inside the bottled is pour into 50 ml scaled flask, and then add collection solution to the volume of 50 ml.
- ii)
- A constant quantity of the sample solution is taken with a syringe. It is injected to the decomposition bottle of the sample decomposition and condensing equipment of 2-(3) through silicon rubber cap. Tri-methyl amine generated by nitrogen flow of 2-3 liter at 0.2-0.3 liter per minute is collected in the sample condenser tube that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen. In the case, blank test is conducted to verify the interfering component by heating sample condenser tube at 70 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow.
- (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
As shown in Fig. 4, the sample condenser tube with trapped subject component that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen, is connected to the gas chromatograph analyzer. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, and verify the stability of the flow rate and the detector sensitivity. Raise the temperature of the condenser tube to 70 degrees Celsius in approximately two minutes. Introduce subject component to the gas chromatograph. - (5) Calibration curve
Tri-methyl amine standard solution that is diluted sequentially with ethyl alcohol or water is injected to the inlet of the gas chromatograph inlet. The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak area of the chromatogram. - (6) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the tri-methyl amine (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) in the liquid separated from the analyzing sample solution by the calibration curve of (5).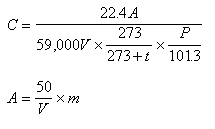
where C is the concentration of the tri-methyl amine in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the tri-methyl amine in the sample solution for analysis (unit : ng), V is the gas volume measured by gas meter (unit : liter), t is temperature at gas meter (unit : degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sampling (unit : kPa), m is the quantity of the tri-methyl amine from the calibration curve and Vis the volume of the solution taken from the sample solution for analysis (unit : ml).
Remarks
- The concentration of the tri-methyl amine is calculated by following equation;

where C is the concentration of the tri-methyl amine (g/liter) and ais the assumption (ml) of hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/liter). - Indication reagent is prepared by mixing 50 ml of bromocresol green solution and 10 ml of methylred solution, that are respectively dissolved 100 mg of bromocresol green and methylred and to dilute to 100ml with ethyl alcohol.
- In case of low content of water in the sample and no sorption effect, sample gas may be collected through operation of 1-3-(2)-i) of the attached table 2 by using the equipment shown in 1-2-(1)-i) and (2) (note 2) of the attached table 2. The sample gas collected in the sampling bag shall be collected as soon as possible through operation of 1-3-(1) (note 3) by using the sampling equipment shown in 1-3-(1) (note 3). Flow rate lower than 10 liter/minute is permitted.
(note 1) The inner volume of the sampling bag shall be approximately 50 liter.
- In case where the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the tri-methyl amine concentration in the exhaust gas measured by method listed in I.
Fig. 1 Condenser tube
- Silicon rubber cap
- Capillary tube
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
- Quartz glass wool
Fig. 2 Sample decomposition and condenser equipment
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow adjust valve
- Contamination trap
- Decomposition bottle
- Desiccater
- Filter
- Condenser tube
Fig. 3 Gas chromatograph analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Contamination trap
- three direction valve
- Condenser tube
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Detector
- Bypass
Attached Table 4
Measurement method of acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, iso-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso- alericaldehyde
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
- Gas chromatograph method
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Acetnitryl (extract)
In case of injection into gas chromatograph, no peak appears in the holding time of acetoaldehyde-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone, propion aldehyde-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone, n-buthyl aldehyde-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone, n-valeric aldehyde-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone and iso-valeric aldehyde-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone (hereinafter referred to "aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone"). - (2) Sodium sulfate
Five grams of sodium sulfate with particle diameter of 150-250 micro meter is heated for four hours at 450 degrees Celsius, and 5 ml of acetnitryl is added. After being filtered, 5 ml of acetnitryl is repeatedly added. After being filtered, the filtered solution is vaporized to concetrate to 50 micro liter and to solved into 1 ml of ethyl acetate. In case of injection into gas chromatograph, no peak appears in the holding time of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone. - (3) Ethyl acetate
In case of injection into gas chromatograph, no peak appears in the holding time of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone. - (4) Ethyl alcohol
In case of injection into gas chromatograph, no peak appears in the holding time of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone. - (5) 2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazine
Recrystallized with solution of acetnitryl and water mixed in the volume ratio of 1 to 3. - (6) Sample collection reagent
Particle octa-desil-siryl silica gel with particle diameter of 35-105 micrometer or equivalent. - (7) Cathion exchange resin
Hydrophilic porous vinyl polymer with particle diameter of 40-100 micrometer or equivalent. - (8) Inner standard solution
Ten milligrams of di-phenyl amine dissolved in ethyl acetate and diluted to 100 ml. - (9) Standard solution of aldehydes
One gram of 2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazine and conc.-sulfuric acid is dissolved in 5 ml of ethyl alcohol for aldehyde listed in column 1 of the following table. The aldehydes listed in column 2 is dissolved in the 5 ml of ethyl alcohol is added to the solution. Suction filtration is made for crystallized material, and it is washed with water and ethyl alcohol, and is desiccated. The crystal that is crysitallized in the ethyl alcohol of the quantity listed in column 3 is dissolved in ethyl acetate (each of them is the standard solution containing 10 mg of aldehyde listed in column 1).Column 1 Column 2(mg) Column 3(mg) Acetaldehyde 220 50.9 Propionaldehyde 290 41.0 n-Buthylaldehyde 360 35.0 Iso-Buthylaldehyde 360 35.0 n-Valericaldehyde 430 30.9 Iso-Valericaldehyde 430 30.9
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler and sampling bag
The same as I-2-(1)-i) and (2) (note 1) of the attached table 2. - (2) Sample collection equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 1 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- Condenser tube
- (i)
- Shape shown in Fig. 2, made of resin and inner diameter of 10 mm and length of 45 mm, and capable of cap for both ends.
- (ii)
- The coating of the sample collection reagent is washed by acetnitryl. The 0.5 mg of reagent that is dried with pressurized or suction nitrogen, is dipped in the 2 ml of ethyl alcohol solution containing 1 mg of 2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazine and 5 mg of phosphoric acid. After eliminating ethyl alcohol solution, the reagent is dried with pressurized or suction nitrogen. Then being dried in the desiccater for 12 hours and dried by nitrogen flow of 50-100 ml per minute. Or the equivalent coating method shall be employed.
- (iii)
- Filling sample collection reagent coated in (ii) to the tube and the glass wool or equivalent is used to clog the both ends to avoid filler lost from the tube.
- ii)
- Sampler pump with air suction power of over 1 liter per minute.
- iii)
- Gas meter is able to measure the flow rate range of 0-1 liter/min.
- (3) Cathion exchange resin tube
- i)
- Shape shown in Fig. 3, made of resin and inner diameter of 10 mm and length of 60 mm, and capable of cap for both ends.
- ii)
- The cathion exchange resin of 0.1g is washed sequentially by 6 ml of water, sodium chloride (l mol/liter), water, hydrochloric acid (1 mol/liter), water, ethyl alcohol, acetnitryl, or equivalent.
- iii)
- 0.1 g of cathion exchange resin prepared in ii) is filled in the tube and the glass wool or equivalent is used to clog the both ends to avoid resin lost from the tube.
- (4) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 4 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- Alkaline thermal ionization detector is equipped with the gas chromatograph or equivalent.
- ii)
- The column is a capillary column made of melted quartz, and inner diameter of 0.2 mm and the length of 25 meter, methyl silicone is coated with the thickness of 0.1 micrometer or equivalent.
- iii)
- The temperature of the sample inlet shall be 250 degrees Celsius.
- iv)
- The column chamber shall be set to the optimum separation condition of the subject component. (For example, maintaining for 1 minute on 50 degrees Celsius, raising temperature from 50 degrees Celsius to 200 degrees Celsius at 25 degrees Celsius per minute for 6 minutes, and raise temperature to 250 degrees at 3 degrees Celsius per minute)
- v)
- The nitrogen or helium is used for carrier gas or make up gas of flow rate of 20-3- ml/minute.
- vi)
- The structure is able to contain the 1 micro liter of the test liquid in the column.
(note 1) Inner volume of the sampling bag shall be 50 liter.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
As shown in Fig. 5, the sample collection tube and the cathion exchange resin tube are connected, 6 ml of the solved liquid drips to the cap type tube (with scale) naturally or in the flow rate of 1 ml/minute. Dehydrate the liquid by adding small amount of sodium sulfate, and vaporized acetnitryl to 50 micro liter (1 drip) by blowing with nitrogen from top of the tube. The acetnitryl is dissolved by adding 1 ml of ethyl acetate, and add 80 micro liter of inner standard solution to make test liquid. Then performing gas chromatograph in the sequence (4) to verify no peak appeared in the holding time of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone. - (2) Gas sampling
Sample gas is collected in the sampling bag in the operation of I-3-(2) of the attached table 2. - (3) Sample collection
As soon as the sample gas is collected, remove the caps at both end of the collection tube. Then, the tube is connected to the sampling bag as shown in Fig. 1. The sample is collected in the bag by absorbing 30 liter at flow rate of 1 liter/minute. (note 2) - (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
The sample collection tube with collected sample is treated in the same manner as (1) (note 3), 1 micro liter of sample is taken with micro syringe to inject from the inlet of the gas chromatograph. In case where the peak is separated for stereoisomer of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone on the chromatogram, the peak area of the subject component is summation of peak area. - (5) Calibration curve
Standard solutions of the aldehydes are diluted sequentially with ethyl acetate. One micro liter of diluted standard solution that is prepared by adding 80 micro liter of inner standard solution with 1 ml of diluted solution is injected to the inlet of the gas chromatograph inlet. By taking ratio (Ax/As) of the peak area (Ax) of chromatogram of aldehydes-2,4-dinitro phenyl hydrazone and the peak area (As) of chromatogram of di-phenyl amine as the vertical axe, and ratio (Mx/Ms) of injection quantity of aldehydes (Mx) and injection quantity of di-phenyl amine (Ms) as the horizontal axe, the calibration curve is plotted in the range of linear relation. - (6) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, iso-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso-Valericaldehyde (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) in the liquid separated from the analyzing sample solution by the calibration curve of (5) (note 4).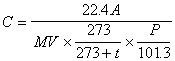
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the sample solution for analysis (unit : ng), V is the gas volume measured by gas meter (unit : liter), t is temperature at gas meter (unit : degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sampling (unit : kPa).
- (note 2)
- Caps shall be applied to both end of the sample collection tube. It shall be covered from the light storage or transportation.
- (note 3)
- Sample collection tube shall be solved by solution as soon as possible.
- (note 4)
- For the quantity (A) of the subject component in the test solution of the sample, the chromatogram is recorded in the same condition by mixing uniformly to control the added quantity of the di-phenyl amine in the range of the calibration curve and by adjusting the volume of test solution in order to control the peak area of the di-phenyl amine to be approximately the same as calibration curve plot. The quantity of the subject component (A) is calculated from the added quantity of di-phenyl amine, by calculating ratio of (A'x/A's) of the peak area of the subject component (A'x) and the peak area of the di-phenyl amine (A's) from the chromatogram and by obtaining ratio of (A/M's) of the quantity of the subject component (A) and the quantity of the di-phenyl amine (M's) from the calibration curve.
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 1 Gas sampling equipment
- Sampling bag
- Sampling tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
Fig. 2 Collecting tube Transportation and storage
- Sample collection reagent
- Quartz glass wool
- Resin cap Aluminum foil
Fig. 3 Cathion exchange resin tube
- Cathion exchange resin
- Quartz glass wool
- Resin cap Aluminum foil
Fig. 4 Gas chromatograph analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Detector
Fig. 5 Solving operation
- Syringe
- Collecting tube
- Cathion exchange resin
- Capped test tube
II. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
- Gas chromatograph mass analysis method
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) N,N-dimethyl formamide
In case of injecting a few micro litter of solution diluted to one tenth concentration with water into gas chromatograph mass analyzer, no peak appears in the holding time of subject component. - (2) Standard solution of aldehydes
Hundred micro liters of aldehyde is dissolved in water or N,N-dimethyl formamide to dilute to 100 ml for type of aldehyde listed in column 1 of the following table. (one micro liter of each solution correspond to the quantity listed in the column 2 (o degree Celsius and 1 atm.) as a gaseous aldehyde listed in the column 1. For acetaldehyde, the containing rate shall be multiplied.)Column 1 Column 2
(unit : micro liter)Acetaldehyde 0.311 Propionaldehyde 0.311 n-Buthylaldehyde 0.249 Iso-Buthylaldehyde 0.247 n-Valericaldehyde 0.211 Iso-Valericaldehyde 0.204 - (3) Porous polymer beads
Polymer beads that absorb hydrocarbons of carbon number greater than 6, release the absorbed component at 200 degrees Celsius, are made of para-phenylen oxide, are in particle diameter range of 180-250 micro meter and are durable at 350 degrees Celsius. - (4) Porous silica beads
Silica beads that absorbs hydrocarbons, release the absorbed component at 200 degrees Celsius, is in particle diameter range of 100-300 micro meter and surface area is 10 mイ/g. - (5) Activated carbon
Particle diameter range of 180-250 micro meter
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler and sampling bag
The same as I-2-(1)-i) and (2) of the attached table 2. - (2) Sample collection equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 6 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- Collecting tube (i) Shape shown in Fig. 7, made of borosilicate glass and inner diameter of 5 mm and length of 18 cm, and capable of attaching syringe needle at the one end of the tube. (ii) After washing the inside of the tube with acetone and being desiccated, 0.2 g of porous polymer beads, 0.2 g of porous silica beads and 0.2 g of activated carbon or equivalent are filled as filler. The glass wool is used to clog the both ends to avoid filler lost from the tube. (iii) The both end of the tube shall be closed with fluoride resin cap and silicon rubber cap.
- ii)
- Sampler pump with air suction power of over 1 liter per minute.
- iii)
- Gas meter is able to measure the flow rate range of 0-1 liter/min.
- (3) Condenser tube
The configuration shown in Fig. 8 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The tube is made of borosilicate glass or fluoride resin and the inner diameter of 4 mm.
- ii)
- After washing the inside the tube with water and desiccated, the white diatomaceous earth with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter, holder of the filler is washed with acid and processed by dimethyl-dichloro silane or equivalent is used as filler.
- iii)
- Aluminum foil is placed on the outside of the tube. It is isolated with glass fiber tape. Thermocouple is attached to measure the temperature. Nickel-chrome wire with glass fiber tube is turned on the same spacing, and fixed with glass fiber tape.
- (4) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 4 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The gas chromatograph includes detector of electron impact ionization (EI method) and selective ion detection (SIM method) or equivalent chromatograph measurement shall be enabled.
- ii)
- Carrier gas path is changed at the sample inlet and is connected to contamination trap and condenser tube.
- iii)
- The column is a capillary column made of melted quartz, and inner diameter of 0.5 mm and the length of 50 meter, methyl silicone is coated with the thickness of 5 micrometer or equivalent.
- iv)
- The temperature of the sample inlet shall be 150 degrees Celsius. v) The column chamber shall be set to the optimum separation condition of the subject component. (For example, raising temperature from 30 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius at 5 degrees Celsius per minute)
- v)
- The helium is used for carrier gas of flow rate of 10 ml/minute.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample collecting tube is heated at 200 degrees Celsius with nitrogen or helium flow of 50 ml/min from the activated carbon side, and this condition is kept for approximately 6 hours. An analysis routine is performed on item (4) to verify no peak in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Gas sampling
Sample gas is collected in the sampling bag by the operation of I-3-(2) in the attached table 2. - (3) Sample collection
As soon as the sample gas is collected, remove the caps made of fluoride resin and silicon rubber at both end of the collection tube. Then, the tube is connected to the sampling bag. The sample is collected in the bag at flow rate of 1 liter/minute from the porous polymer beads. (note 5) - (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
As shown in Fig. 10, the sample condenser tube that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen, is connected to the gas collection tube. By heating the sample collecting tube to 150 degrees Celsius, and this condition is kept for 5 minutes, with nitrogen or helium flow of 50 ml/min, the subject component is moved to the condenser tube. As shown in Fig. 9, the condenser tube with subject component is connected to the chromatograph analyzer. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, raise the temperature of the condenser tube to 150 degrees Celsius in short time. Introduce subject component to the gas chromatograph. (note 6) - (5) Calibration curve The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak area of the chromatogram of the selective ion detection method on the same operation (4), by injecting a few micro liter of aldehydes standard solution from the porous polymer beads side at room temperature.
- (6) Calculating concentration The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, iso-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso-Valericaldehyde (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) in the liquid separated from the analyzing sample solution by the calibration curve of (5).
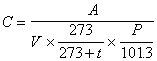
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the sample solution for analysis (unit : ng), V is the gas volume measured by gas meter (unit : liter), t is temperature at gas meter (unit : degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sampling (unit : kPa).
- (note 5)
- Caps shall be applied to both end of the sample collection tube. It shall be covered from the light storage or transportation. The sample collecting tube is refrigerated as soon as possible.
- (note 6)
- Ions of mass number 44 is monitored for acetaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso-Valericaldehyde, ions of mass number 58 or 29 is monitored for propionaldehyde and ions of mass number 72 is monitored for iso-buthylaldehyde
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
III. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the concentration of acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, n-buthylaldehyde, iso-buthylaldehyde, n-valericaldehyde and iso-Valericaldehyde in the exhaust gas measured by method listed in I and II. In case of using the method listed in I above, two collecting tubes in series are used and flow rate shall be adjusted.
Remarks
Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 6 Sampling equipment
- Sampling bag
- Sampling tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
Fig. 7 Collecting tube
Analyzing
Direction of heated degas
Direction of sample collection
- Silicon rubber cap
- Quartz glass wool
- Activated carbon
- Porous silica beads
- Porous polymer beads
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
Transportation and storage
Aluminum foil
- Fluoride resin cap
- Quartz glass wool
- Activated carbon
- Porous silica beads
- Porous polymer beads
Fig. 8 Condenser tube
- Silicon rubber cap
- Capillary tube
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
- Quartz glass wool
Fig. 9 Gas chromatograph mass analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph mass analyzer
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Gas chromatograph mass analyzer
- Condenser tube
- Three direction valve
- Bypass
Fig. 10 Condensing operation
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Liquid oxygen
- Sample collecting tube
- Furnace of sample collecting tube
- Condenser tube
Attached Table 5
Measurement method of iso-Buthylalcohol
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) n-penthan
No peak shall appear in the holding time of iso-buthylalcohol, when it is injected in gas chromatograph. - (2) Standard solution of iso-buthylalcohol
The standard solution of iso-buthylalcohol is prepared by dissolving iso-buthylalcohol in n-penthane and to dilute to 100 ml.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler and sampling bag
The same as I-2-(1) and (2) in the attached table 2. - (2) Condenser tube
The configuration shown in Fig.. 1 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The tube is made of borosilicate glass or fluoride resin and the inner diameter of 4 mm.
- ii)
- After washing the inside the tube with acetone and water and desiccated, the white diatomaceous earth with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter, holder of the filler is washed with acid and processed by dimethyl-dichloro silane or equivalent is used as filler.
- iii)
- Aluminum foil is placed on the outside of the tube. It is isolated with glass fiber tape. Thermocouple is attached to measure the temperature. Nickel-chrome wire with glass fiber tube is turned on the same spacing, and fixed with glass fiber tape.
- (3) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig. 2 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The gas chromatograph includes hydrogen flame ion detector.
- ii)
- Carrier gas path is changed at the sample inlet and is connected to contamination trap and condenser tube.
- iii)
- The column is made of glass and the inner diameter of 3 mm and length of 3 meters. Inner side is washed with acetone and water, and desiccated.
- iv)
- The white diatomaceous earth holder of the filler with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter is coated with 25% of poly-ethylene glycol. Or equivalent filler is used for the purpose.
- v)
- Temperature at the sample inlet shall be 180 degrees Celsius.
- vi)
- The column chamber shall be set to the optimum separation condition of the subject component. (For example, raising temperature from 30 degrees Celsius to 120 degrees Celsius at 5 degrees Celsius per minute)
- vii)
- Nitrogen is employed for carrier gas of flow of 40-50 ml per minute.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample condenser tube is heated for approximately 10 minutes at 200 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow. An analysis routine is performed on item (4) to verify no peak in the holding time of the iso-buthylalcohol. - (2) Gas sampling
Gas is collected in the sampling bag by the operation of I-3-(2) of the attached table 2. - (3) Sample condensing
As shown in Fig. 3, the iso-buthylalcohol in the sampling bag is collected in the sample condenser tube for constant quantity of sample by connecting sampling bag to sample condenser tube that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen. - (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
As shown in Fig. 2, the sample condenser tube with trapped the iso-buthylalcohol, that is cooled with coolant such as liquid oxygen, is connected to the gas chromatograph analyzer. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, and verify the stability of the flow rate and the detector sensitivity. Raise the temperature of the condenser tube to 200 degrees Celsius in approximately two minutes. Introduce the iso-buthylalcohol to the gas chromatograph. - (5) Calibration curve
The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak area of the chromatogram on the same operation (4), by injecting a few micro liter of iso-buthylalcohol standard solution that is sequentially diluted with n-penthane. - (6) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the iso-buthylalcohol (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) collected in the condenser tube by the calibration curve of (5).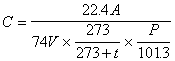
where C is the concentration of the iso-buthylalcohol in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the iso-buthylalcohol in the condenser tube (unit : micro gram), V is the gas volume collected in condenser tube (unit : liter), t is temperature at the sample condensing (unit : degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sample condensing (unit : kPa).
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with ethyl acetate, methyl-iso-buthylketone, and toluene, stylene and xylene.
- For the calibration curve, iso-buthyl alcohol calibration gas may be used in the same manner as the First-1 of the attached table 2. (4 micro liter of iso-buthyl alcohol corresponds to 0.969 ml of gas(0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.))
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the iso-buthyl alcohol concentration in the exhaust gas measured by method of listed in I.
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with ethyl acetate, methyl-iso-buthylketone, and toluene and xylene.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 1 Condenser tube
- Silicon rubber cap
- Capillary tube
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
- Quartz glass wool
Fig. 2 Gas chromatograph analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Detector
- Condenser tube
- three direction valve
- Bypass
Fig. 3 Condensing method
or
- Sampling bag
- Condenser tube
- Fluoride resin tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
- Syringe
Attached Table 6
Measurement method of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
- low temperature condensing
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) n-penthan
No peak shall appear in the holding time of iso-buthylalcohol, when it is injected in gas chromatograph. - (2) Standard solution of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone
The standard solutions of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone are prepared by dissolving 1 g of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone in n-penthane and to dilute to 100 ml.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus the same as I-2 of the attached table 5. The white diatomaceous earth with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter, holder of the filler is washed with acid and processed by dimethyl-dichloro silane and coated 25% with Uconoil 50LB550X or equivalent is used as filler. The column temperature shall be 90 degrees Celsius.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in the process defined in I-3-(1) through (5) in the attached table 5 ("iso-buthyl alcohol" is treated as "ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone") and the calculation methods for concentration are shown as follows;
Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) collected in the condenser tube by the calibration curve.
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit : ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the condenser tube (unit: micro gram), V is the gas volume collected in condenser tube (unit: liter), t is temperature at the sample condensing (unit: degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sample condensing (unit: kPa).
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with iso-buthyl alcohol, toluene, stylene and xylene.
- For the calibration curve, iso-buthyl alcohol calibration gas may be used in the same manner as the First-1 of the attached table 2. (4 micro liter of ethylacetate corresponds to 0.969 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) and 6 micro liter of methyl-iso-buthylketone corresponds to 1.07 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.))
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
- room temperature absorbing
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Standard solution of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone
The same as I-1. - (2) Porous polymer beads
The same as II-1-(3) in the attached table 4.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Gas sampler and sampling bag
The same as II-2-(1) and (2) in the attached table 4. - (2) Sample collection equipment
The same as II-2-(2) in the attached table 4. However, the 0.6 gram of porous polymer beads shall be filled in the sample collection tube. - (3) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The same as I-2. However, the collecting tube can be heated in the heating furnace by connecting a collecting tube equipped a syringe needle to the gas chromatograph instead of condenser tube.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample condenser tube is heated at 230 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow. An analysis routine is performed on item (4) to verify no peak in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Gas sampling
Gas is collected in the sampling bag by the operation of I-3-(2) of the attached table 2. - (3) Sample condensing
As soon as the sample gas is collected, remove the caps made of fluoride resin and silicon rubber at both end of the collection tube. Then, the tube is connected to the sampling bag as shown in Fig. 1. The subject component is collected in the collection tube at constant quantity of flow. - (4) Gas chromatograph analysis
The sample condenser tube with trapped the subject component is connected to the gas chromatograph analyzer. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, and verify the stability of the flow rate and the detector sensitivity. Raise the temperature of the condenser tube to 200 degrees Celsius in approximately one minute. Introduce the subject component to the gas chromatograph. - (5) Calibration curve
The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak area of the chromatogram on the same operation (4), by injecting a few micro liter of ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone standard solution that is sequentially diluted with n-penthane. - (6) Calculating concentration
The concentration of subject component in the air is calculated by method of I-3 with the calibration curve of (5). "Condenser tube" is treated as "sample collecting tube" and "sample condensing" as "sample collecting".
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with toluene, stylene and xylene.
- For the calibration curve, subject component calibration gas may be used in the same manner as the First-1 of the attached table 2. (4 micro liter of ethylacetate corresponds to 0.969 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) and 6 micro liter of methyl-iso-buthylketone corresponds to 1.07 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.))
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
III. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone concentrations in the exhaust gas measured by method of listed in I.
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with ethyl acetate, iso-buthyl alcohol, toluene and xylene.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 1 Gas sampling equipment
- Sampling bag
- Sampling tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
Attached Table 7
Measurement method of toluene, stylene and xylene
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
- low temperature condensing
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) n-penthan
No peak shall appear in the holding time of iso-buthylalcohol, when it is injected in gas chromatograph. - (2) Standard solution of toluene, stylene and xylene
The standard solutions of toluene, stylene and xylene are prepared by dissolving 1 g of isomers (o-, m- and p-) of toluene, stylene and xylene in n-penthane and to dilute to 100 ml.
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus the same as I-2 of the attached table 5. The white diatomaceous earth with particle diameter of 180-250 micro meter, holder of the filler is washed with acid and processed by dimethyl-dichloro silane and coated 5% with SP-1200 and 1.75% with Benton 34 or equivalent is used as filler. The column temperature shall be 40-100 degrees Celsius.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in the process defined in I-3-(1) through (5) in the attached table 5 ("iso-buthyl alcohol" is treated as "toluene, stylene and xylene") and the calculation method for concentration is shown as follows;
Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the toluene, stylene and xylene (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) collected in the condenser tube by the calibration curve. For xylene, the summation of the concentration of all the isomers is considered to be the concentration of the xylene.
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit: ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the condenser tube (unit: micro gram), V is the gas volume collected in condenser tube (unit: liter), t is temperature at the sample condensing (unit: degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the sample condensing (unit: kPa).
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with iso-buthyl alcohol, ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone.
- For the calibration curve, subject component calibration gas may be used in the same manner as I-1 of the attached table 2. (5 micro liter of toluen corresponds to 1.06 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of stylene corresponds to 0.975 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of o-xylene corresponds to 0.928 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of m-xylene corresponds to 0.916 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) and 5 micro liter of p-xylene corresponds to 0.908 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.)) 4 Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
II. Concentration measurement at the border of the site - room temperature absorbing
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Standard solution of toluene, stylene and xylene
The same as I-1. - (2) Porous polymer beads
The same as II-1-(3) in the attached table 4.
2. Equipment and apparatus
The same as II-2 in the attached table 6.
3. Measurement process
Measurement of the concentration is the same as II-3-(1) through (5) in the attached table 6. "ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone" is treated as "toluene, stylene and xylene". The concentration is calculated by method of I-3. "Condenser tube" is treated as "sample collecting tube" and "sample condensing" as "sample collecting".
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with iso-buthyl alcohol, ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone.
- For the calibration curve, subject component calibration gas may be used in the same manner as I-1 of the attached table 2. (5 micro liter of toluen corresponds to 1.06 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of stylene corresponds to 0.975 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of o-xylene corresponds to 0.928 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.), 5 micro liter of m-xylene corresponds to 0.916 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.) and 5 micro liter of p-xylene corresponds to 0.908 ml of gas (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.))
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
III. Flow rate measurement at the gas emission point
The flow rate at the gas emission point is calculated by multiplying gas quantity measured by method of JIS Z8808 to the toluene, stylene or xylene concentration in the exhaust gas measured by method of listed in I and II.
Remarks
- In case where the qualitative analysis is enabled, a part of the sampled gas is taken in the gas syringe, and may be directly injected to sample inlet.
- In case where no interfering substances exists and the separate quantitative analysis is enable, capillary column may be used with iso-buthyl alcohol, ethylacetate and methyl-iso-buthylketone.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Attached Table 8
Measurement method of propionic acid, n-butyric acid, n-valeric acid and iso-valeric acid
I. Concentration measurement at the border of the site
1. Reagent
Reagent shall be prepared in the manner listed below.
- (1) Formic acid
No peak shall appear in the holding time of subject component, when it is injected in gas chromatograph. - (2) Standard solution of propionic acid
The standard solutions of propionic acid are prepared by dissolving 1.0 ml of propionic acid and to dilute to 100 ml. (1 micro liter of this solution corresponds to 3.02 micro liter of gaseous propionic acid (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.)) - (3) Standard solution of n-butyric acid
The standard solutions of n-butyric acid are prepared by dissolving 1.0 ml of n-butyric acid and to dilute to 100 ml. (1 micro liter of this solution corresponds to 2.43 micro liter of gaseous n-butyric acid (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.)) - (4) Standard solution of n-valeric acid
The standard solutions of n-valeric acid are prepared by dissolving 1.0 ml of n-valeric acid and to dilute to 100 ml. (1 micro liter of this solution corresponds to 2.06 micro liter of gaseous n-valeric acid (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.)) - (5) Standard solution of iso-valeric acid
The standard solutions of iso-valeric acid are prepared by dissolving 1.0 ml of iso-valeric acid and to dilute to 100 ml. (1 micro liter of this solution corresponds to 2.04 micro liter of gaseous iso-valeric acid (0 degree Celsius and 1 atm.))
2. Equipment and apparatus
Equipment and apparatus are listed as follows;
- (1) Sampling equipment
The configuration is shown in Fig. 1 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- Collecting tube
- (i)
- The tube is made of borosilicate glass and the inner diameter of 7-8 mm and the length of 10 cm, syringe needle can be connected at one end of the tube as shown in Fig. 2.
- (ii)
- The tube is washed with phosphoric acid (1+4) and water, and is desiccated, then the 3 g of filler is filled in the tube, and quartz glass wool is used to clog the both ends to avoid filler lost from the tube.
- (iii)
- The glass beads with particle diameter of 500-1180 micro meter are washed with hydrochloric acid (1+3) and water, then desiccated and coated 1% of strontium hydroxide. Coating is made by strontium hydroxide of 1 % weight of glass beads that is dissolved with small amount of water, is mixed with glass beads on the ceramic dish and quickly dried or equivalent.
- (iv)
- The both end of the tube shall be closed with fluoride resin cap and silicon rubber cap.
- ii)
- Sampler pump with air suction power of over 5 liter per minute.
- iii)
- Gas meter is able to measure the flow rate range of 0-10 liter/min.
- (2) Gas chromatograph analysis equipment
The configuration shown in Fig.. 3 and the following condition is satisfied.- i)
- The gas chromatograph includes hydrogen flame ion detector.
- ii)
- Carrier gas path is changed at the sample inlet and is connected to contamination trap and condenser tube.
- iii)
- The column is made of glass and the inner diameter of 3 mm and length of 3 to 5 meters. Inner side is washed with phosphoric acid and water, and desiccated.
- iv)
- The carbon black holder with particle diameter of 180-250 micrometers, that is coated with 0.3% of FFAP and 0.3% of phosphoric acid is used as filler. Or equivalent filler is used for the purpose.
- v)
- Temperature at the sample inlet shall be 230 degrees Celsius.
- vi)
- Temperature at the column chamber shall be controllable in the range of 80-200 degrees Celsius.
- vii)
- Nitrogen is employed for carrier gas of flow of 40-50 ml per minute.
3. Measurement process
Concentration measurement is performed in following process;
- (1) Blank test
Sample collecting tube is heated at 300 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes. Connect the collection tube to the gas chromatograph. With nitrogen flow of 50 ml/min, 20 micro liter of 5 % formic acid is injected to verify no peak appeared in the holding time of the subject component. - (2) Sample collection
By removing the caps made of fluoride resin and silicon rubber at both end of the collection tube. The sample is collected in the tube at flow rate of 5 liter/minute for 5 minutes. - (3) Gas chromatograph analysis
A syringe needle is connected to the gas collection tube. By heating the sample collecting tube to 180 degrees Celsius with nitrogen flow of 50 ml/min. As shown in Fig. 9, the collecting tube is connected to the chromatograph analyzer, after cooling to room temperature. Then, flow carrier gas through the sample condenser tube, and verify the stability of the flow rate and the detector sensitivity. Raise the temperature of the collecting tube to 180 degrees Celsius in approximately 1 minute. Introduce subject component to the gas chromatograph. The column temperature is raised from 80 to 200 degrees Celsius in 10 minutes. - (4) Calibration curve
The calibration curve is plotted according to the peak area of the chromatogram on the same operation (3), by injecting a few micro liter of propionic acid, n-butyric acid, n-valeric acid and iso-valeric acid standard solutions diluted in sequence. - (5) Calculating concentration
The concentration in the air is calculated by following equation by using quantity of the propionic acid, n-butyric acid, n-valeric acid and iso-valeric acid from the calibration curve of (4).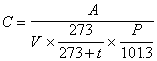
where C is the concentration of the subject component in the air (unit: ppm), A is quantity of the subject component in the sample collecting tube (unit: micro gram), V is the gas volume measured by gas meter (unit: liter), t is temperature at gas meter (unit: degree Celsius), P is the atmospheric pressure at the gas sampling (unit: kPa).
Remarks
- In case of low content of water in the sample and no sorption effect, sample gas may be collected through operation of I-3-(2)-i) of the attached table 2 by using the equipment shown in I-2-(1)-i) and (2) (note 1)of the attached table 2. The sample gas collected in the sampling bag shall be collected as soon as possible through operation of 1-3-(2) by using the sampling equipment shown in 2-(1).
(note 1) The inner volume of the sampling bag shall be approximately 50 liter.
- Terminology and other items in this measurement method that are not defined, shall follow the definition of Japan Industrial Standard.
Fig. 1 Gas sampling equipment
- Collecting tube
- Suction pump
- Gas meter
Fig. 2 Gas sampling equipment
- Silicon rubber cap
- Quartz glass wool
- Alkaline beads
- Cap made of fluoride resin
- Syringe needle made of stainless steel
Fig. 3 Gas chromatograph analyzer
Main body of gas chromatograph
- Nitrogen bottle
- Flow meter
- Flow adjust valve
- three direction valve
- Collection tube
- Furnace for collection tube
- Sample inlet
- Column
- Detector
- Bypass