Instruments for Measuring External Exposure
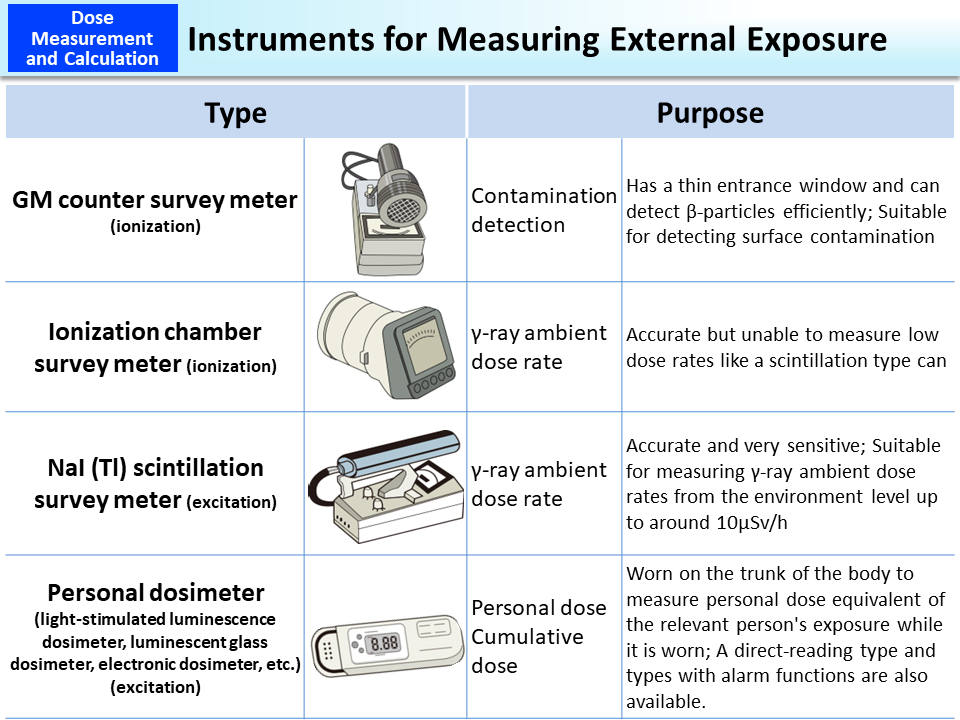
Survey meters are either for inspecting body surface contamination or for measuring ambient dose rates. Geiger Muller (GM) tube-type survey meters are highly sensitive to β-particles and are thus suitable for inspecting body surface contamination. They are relatively affordable and useful in locating contamination and confirming the effects of decontamination.
Ionization chambers are most suited for measuring high-level ambient dose rates but cannot measure very low dose rates. Therefore, a scintillation type is most suited for measuring ambient dose rates in the general environment.
NaI (Tl) scintillation survey meters can also measure the radioactivity intensity, but measurement results vary depending on the level of radiation at the measuring location and the way of measurement. Since calibration at a facility with a radioactive source that serves as a reference is required before converting the measurement results into becquerels, expert assistance is required to implement the measurements.
Personal dosimeters provide cumulative exposure dose readings. An electronic direct-reading type allows a person to confirm the degree of exposure at certain time intervals or after every operation.
- Included in this reference material on March 31, 2013
- Updated on March 31, 2019